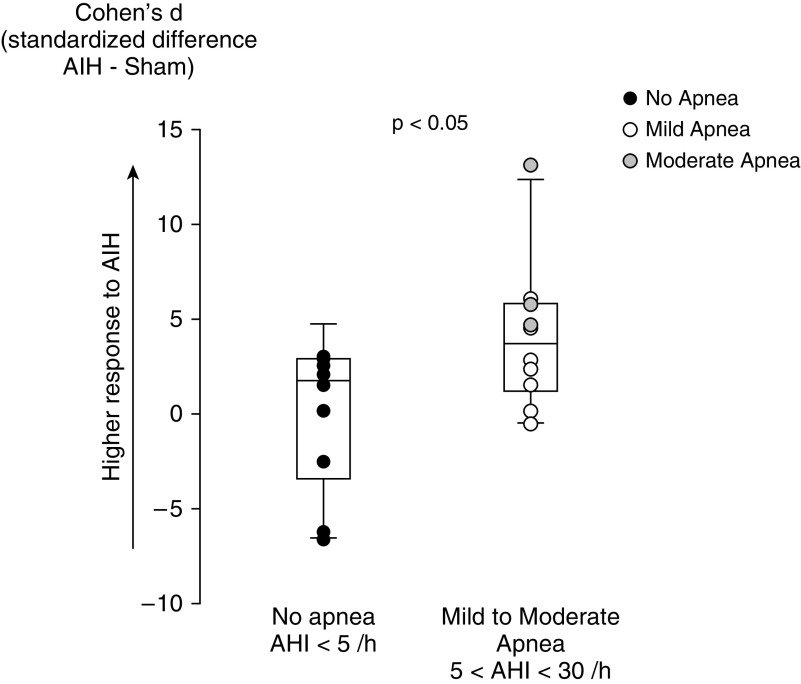
Figure 1.
Effect of sleep-disordered breathing (as assessed by the apnea–hypopnea index [AHI]) on the response to acute intermittent hypoxia (AIH) therapy. Shown are individual values and box plot (median, 10th, 25th, 75th, and 90th percentiles with error bar) of Cohen’s d in individuals with incomplete spinal cord injury and sleep apnea (mild to moderate apnea 5 < AHI < 30/h) or no apnea (AHI < 5/h).