Figure 8.
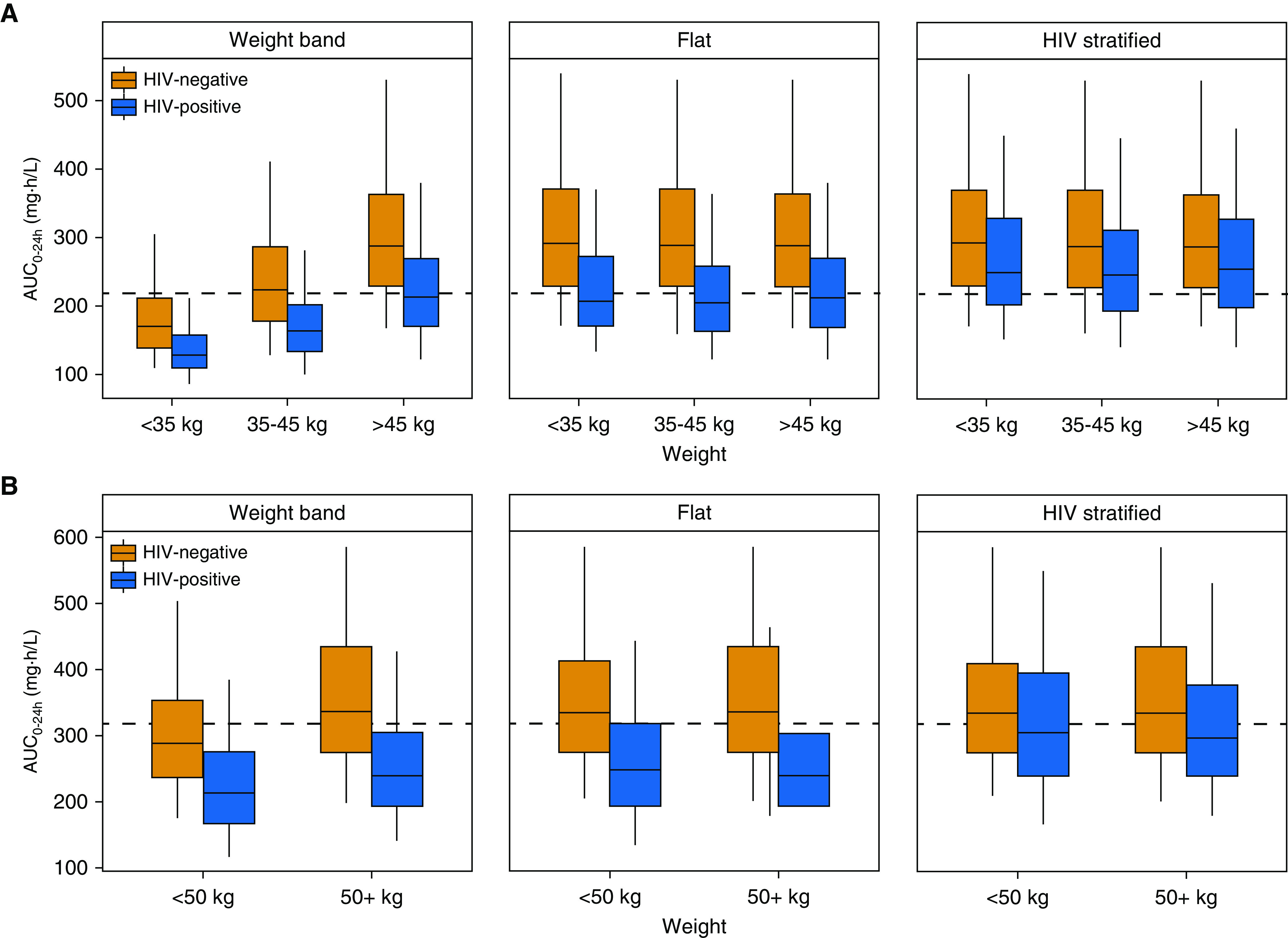
Predicted rifapentine exposures with different dosing methods for (A) a regimen of daily isoniazid-rifapentine for 1 month (1HP) and (B) a regimen of once-weekly rifapentine-isoniazid for 3 months (3HP). Profiles for drug-exposure area under the concentration–time curve over 24 hours (AUC0–24h) are based on 500 simulations. (A) 1HP predictions reflect steady-state exposures to account for autoinduction. “Weight-band” rifapentine doses were 300 mg for <35 kg, 450 mg for 35–45 kg, and 600 mg for >45 kg, as currently recommended for 1HP. The “flat” approach prescribed 600 mg to all individuals, and the “HIV-stratified” approach increased the dose in HIV-positive individuals to 750 mg. (B) 3HP doses were 750 mg for <50 kg and 900 mg for ≥50 kg for the weight-band approach, as currently recommended. The flat approach prescribed 900 mg to all individuals, and the HIV-stratified approach increased the dose in HIV-positive individuals to 1,200 mg. Dashed lines represent (B) the median AUC0–24h (317 mg · h/L) observed in patients treated with 3HP in the PREVENT-TB trial (i.e., TBTC-26 [Tuberculosis Trials Consortium Study 26]) and (A) the median predicted AUC0–24h in HIV-positive patients with 600 mg daily (219 mg · h/L).
