Figure 1. GRIK1 rs2832407 A/A and C/C iPSCs differentiate into functional neurons.
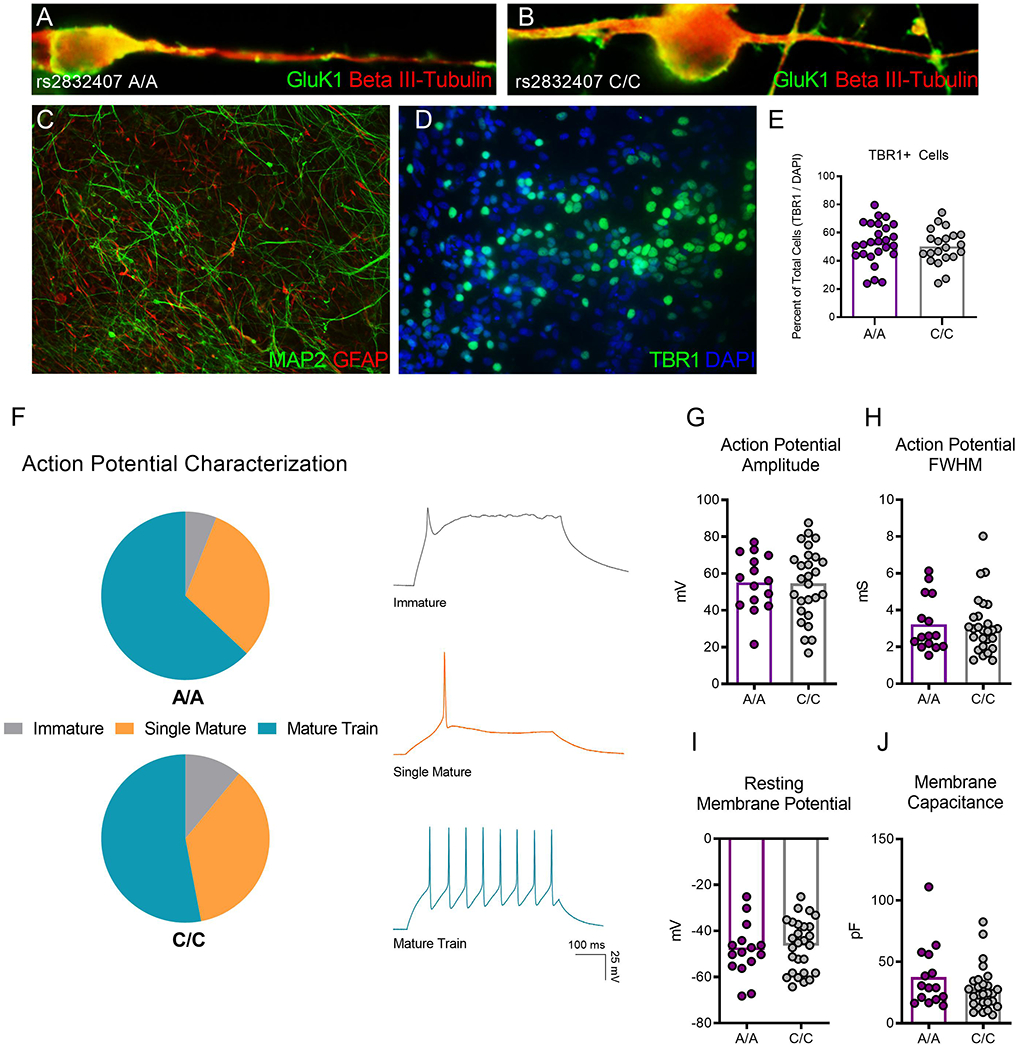
(A-B) A/A and C/C neurons 12 weeks after plating express GluK1 (green), which can be observed localizing to the soma and along beta-III tubulin positive neurites. (C) Neural differentiation produces mixed cultures containing MAP2-positive neurons and GFAP-positive astrocytes. (D-E) Cultures are enriched for TBR1-positive glutamate neurons. The percentage of TBR1-positive cells relative to the total cell population does not differ in neural cultures derived from 3 A/A and 5 C/C donors. 7,163 total cells total were counted for analysis. (F) iPSC-derived neurons (17-19 weeks post plating) generate mature action potential trains in response to a depolarizing current injection. The percentage of neurons that generate immature, single mature, or mature action potentials did not differ between 1 A/A and 2 C/C donors. Example traces for each action potential category are shown. (G-J) No difference between GRIK1 genotypes was observed in neuronal properties including (G) action potential amplitude, (H) action potential full width at half-maximum (FWHM), (I) resting membrane potential, and (J) membrane capacitance. Each dot on the graphs depicting distribution represents an individual neuron.
