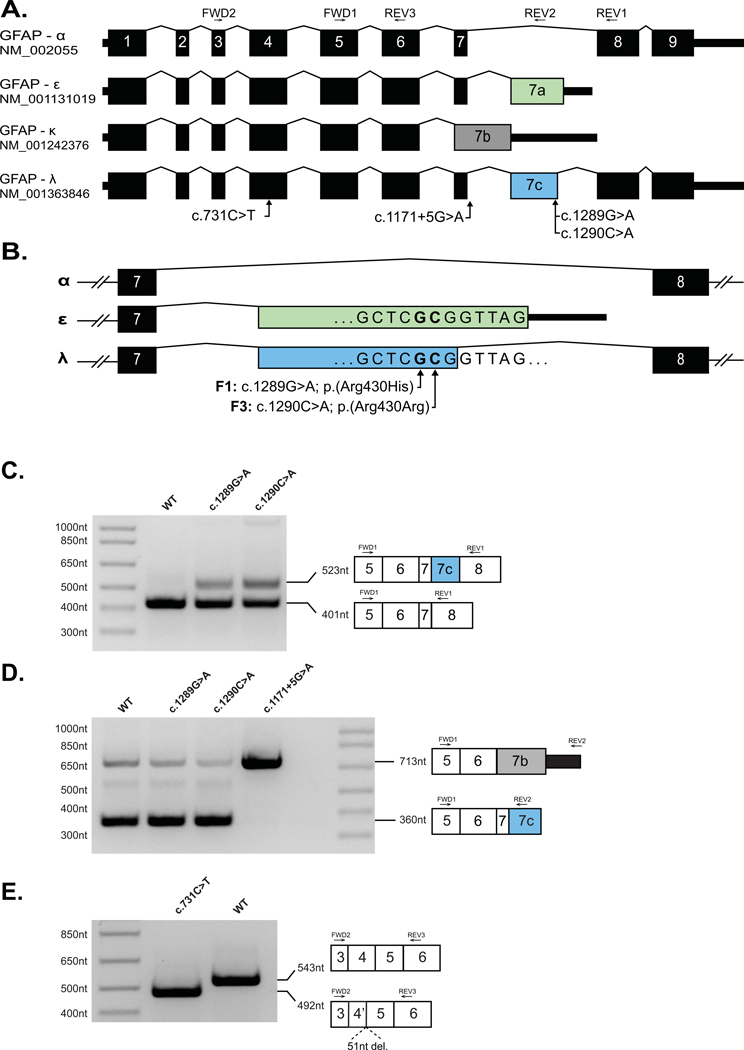
Figure 1: Missense and synonymous variants in GFAP result in alteration in GFAP pre-mRNA splicing.
(A) Schematic of four GFAP mRNA isoforms. Exons 1–9 are numbered per the GFAP-α isoform. Introns are not shown to scale. (B) Schematic of C-terminal variants between exons 7–8 of GFAP showing the positions of the single nucleotide substitutions identified in Family 1 (F1) and Family 3 (F3) relative to exon 7A (green, GFAP-ε) and exon 7C (blue, GFAP-λ). (C) A GFAP mini-gene plasmid was created by introducing 8.1kb of GFAP genomic DNA (exon1 – exon 9, amino acids 57–433) into the mammalian expression vector pEYFP-C1 (see Methods). Versions of this construct were generated containing the GFAP-ε variants, c.1289G>A and c.1290C>A, or the GFAP-α variants c.731C>T and c.1171+5G>A variants before transfection into HEK cells. rtPCR amplification from exon 5 to exon 8 yielded a predominant amplicon consistent with the GFAP-α isoform (401nt) from the WT (Lane 1) c.1289G>A (Lane 2) and c.1290C>A (Lane 3) constructs. The c.1289G>A and c.1290C>A mutant constructs also generated a larger amplicon consistent with the GFAP-λ isoform (523nt). (D) Amplification from exon 5 to exon 7A/7C yielded a predominant amplicon consistent with the GFAP-ε and GFAP-λ isoforms (360nt) from the WT (Lane 1), c.1289G>A (Lane 2) and c.1290C>A (Lane 3) constructs, and a minor amplicon consistent with the GFAP-κ (713nt) is also visible in each of these lanes. The c.1171+5G>A mutant construct yielded a single predominant amplicon consistent in size with GFAP-κ (713nt). (E) Amplification from exon 3 to exon 5 (common to all major GFAP isoforms) yielded a single amplicon consistent with the expected size of 543nt from the WT construct (Lane 2). Amplification from the construct containing the c.731C>T missense variant (Lane 1) yielded a smaller single amplicon consistent with a truncation of exon 4. Sanger sequencing of the c.731C>T amplicon confirmed a 51nt truncation of exon 4 (Supp. Figure S3).