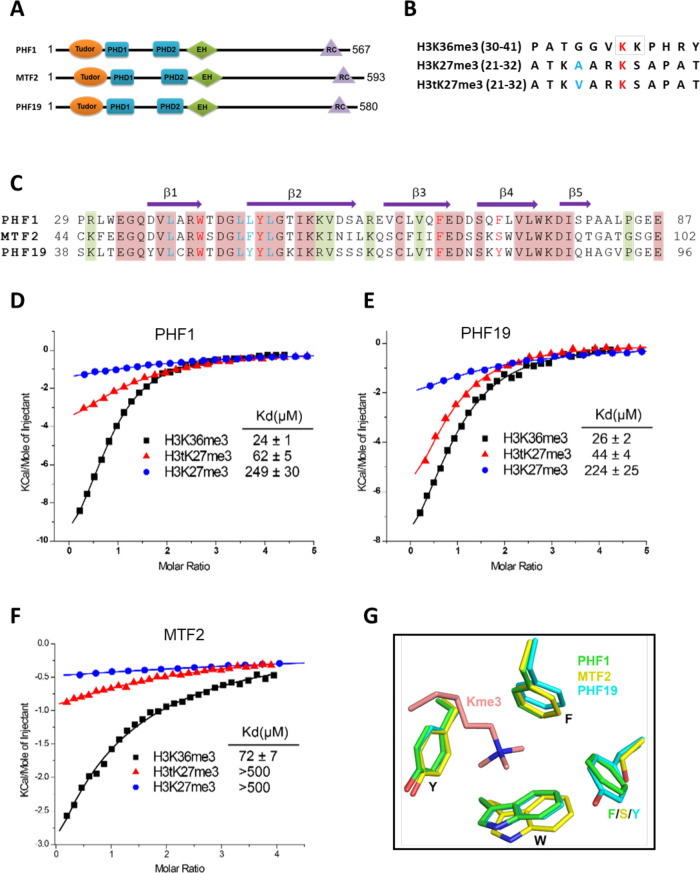
Figure 1. Tudor domains of PHF1 and PHF19 preferentially recognize H3K36me3 and H3tK27me3.
(A) Schematic representation of domain structures of PHF1, MTF2, and PHF19. PHD: plant homeodomain finger. EH: extended homologous domain. (B) Peptide sequences of H3K36me3, H3K27me3, and H3tK27me3. The methylated lysines are colored in red. A24 of histone H3 and V24 of histone H3t are colored in blue. (C) Sequence alignment of the Tudor domains of PHF1, MTF2, and PHF19. The secondary structure elements are shown above the alignment. Identical residues and conserved residues are highlighted in red and olive-green backgrounds, respectively. The residues forming the aromatic cage and the leucyl patch are colored in red and blue, respectively. (D-F) ITC measurements of the interactions of the Tudor domains of PHF1, PHF19, and MTF2 with the H3K36me3, H3tK27me3, and H3K27me3 peptides. (G) Superposition of the aromatic cage residues of PHF1-H3tK27me3 complex (green, this study), MTF2-H3K36me3 (yellow, PDB: 5XFR), and PHF19-H3tK27me3 complex (cyan, this study). The trimethyl-lysine is shown as salmon sticks.