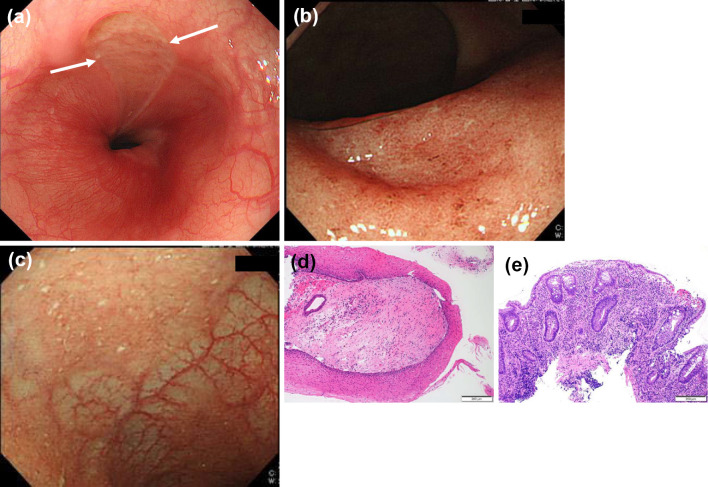
Figure 3.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), colonoscopy, and their pathological findings. (a) EGD showing a longitudinal ulcer in the lower esophagus. (b) Colonoscopy showing mucosal friability in the rectum. (c) Colonoscopy showing mucosal friability in the terminal ileum. (d) Biopsy specimen from the esophageal ulcers showing infiltration of inflammatory cells in the epithelia [Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining, ×100]. (e) Biopsy specimen from the rectum showing inflammatory cell infiltration with basal plasmacytosis and cryptitis (H&E staining, ×100).