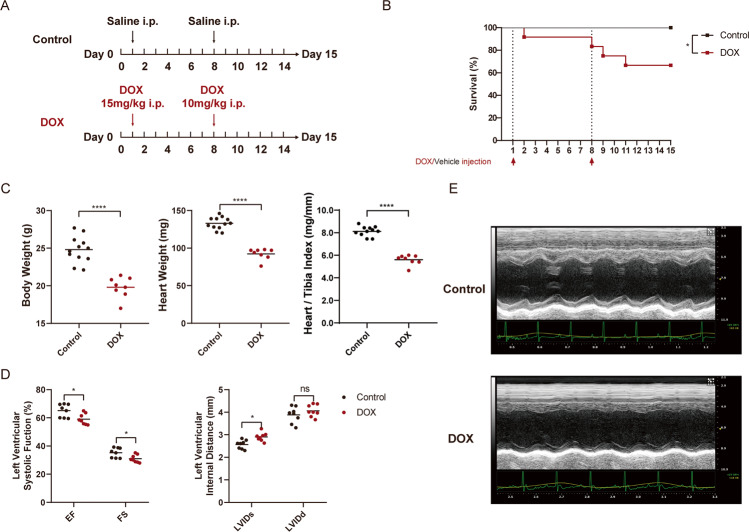
Fig. 1. DOX causes significant cardiac dysfunction and death in mice.
a The protocol of DOX-induced sub-chronic cardiotoxicity model establishment. Mice were treated with saline (vehicle control, N = 12) or DOX (N = 12) on Day 1 (15 mg/kg DOX, i.p) and Day 8 (10 mg/kg, i.p). b Kaplan–Meier survival curves of control and DOX-treated mice during treatment. c The heart/body weight ratio was measured in control mice and DOX-treated mice. d Echocardiographic analyses of cardiac function in control mice and DOX-treated mice. EF ejection fraction, FS fractional shortening, LVIDs systolic left ventricular internal diameter, LVIDd diastolic left ventricular internal diameter. e Representative echocardiograms from control and DOX-treated mice on Day 15. Significance in b was calculated using the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. Significance in c, d was calculated using the unpaired Student’s t test. P value < 0.05 was considered to be significant, and labeled as *P < 0.05; ****P < 0.001; ns not significant.