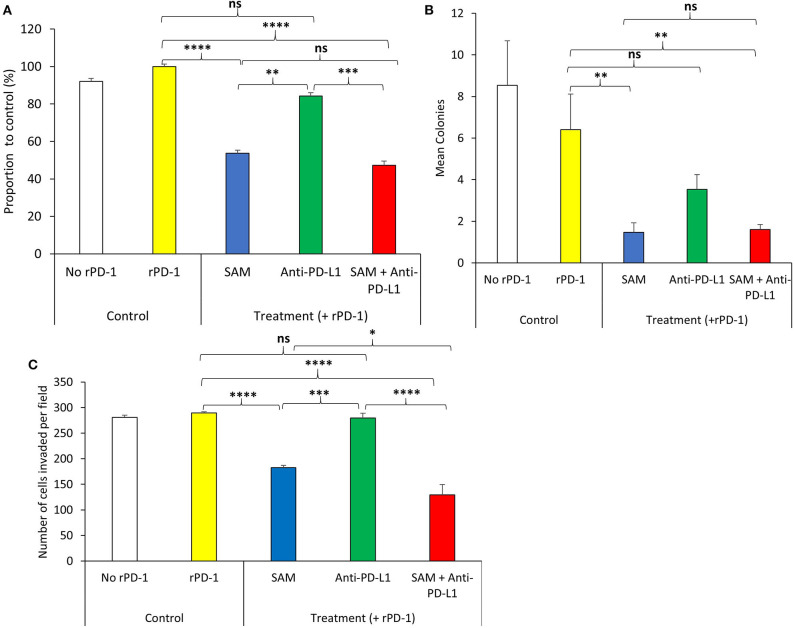
Figure 1.
Effect of SAM and anti-PD-L1 antibody on B16-F1 melanoma cell proliferation, colony formation, and invasion in vitro. B16-F1 cells (2 × 104 cells) were seeded in 6-well plates and were stimulated with rPD-1. The experiment had five treatment groups: No rPD-1 added (control no rPD-1), 0.2 μM rPD-1 control (Control with rPD-1), treated with 0.2 μM rPD-1 followed by treatment with 200 μM SAM (SAM), 50 μg/mL of anti-PD-L1, or combination of SAM+anti-PD-L1, and cells were subjected to proliferation, colony formation, and invasion assay as described in Materials and Methods. (A) Proliferation is presented as the percentage of rPD-1 Control ± SEM. (B) Colony formation is presented as mean ± SEM. (C) Invasion assay is presented as mean number of cells invaded per field ± SEM. Results are mean of at least two independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA in GraphPad prism and are represented by asterisks (ns, not significant, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001).