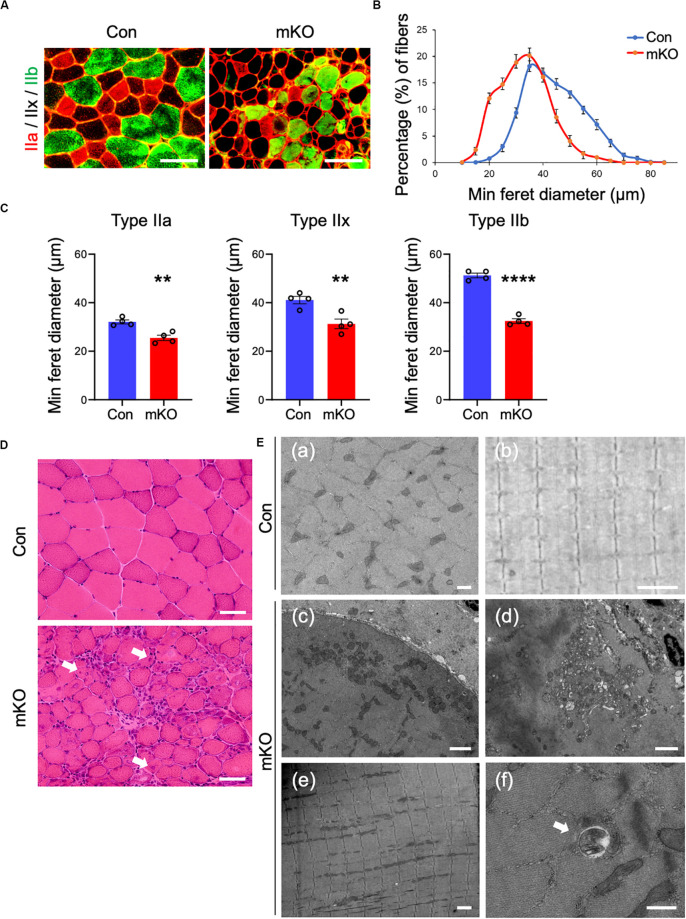
FIGURE 3.
Muscle fiber sizes in muscle-specific Rpt3-deficient mice. (A) Immunohistochemical staining for myosin heavy chain type IIa (red), type IIb (green), and type IIx (unstained) in the tibialis anterior muscles of Con and mKO mice after doxycycline (DOX) treatment. Scale bar = 100 μm. (B) Distribution of muscle fiber minimal Feret’s diameters in the tibialis anterior muscles of Con and mKO mice. Data represent the means ± SEM (n = 4 per group). (C) Quantification of the minimal Feret’s diameter by the fiber type (IIa, IIx, and IIb) in the tibialis anterior muscles of Con and mKO mice. Data represent the means ± SEM (t-test: **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001; n = 4 per group). (D) H&E staining of the tibialis anterior muscles from Con and mKO mice. Arrows indicate the central nuclei in myofibers. Scale bar = 50 μm. (E) Electron micrographs of the tibialis anterior muscles from Con and mKO mice. (a) Cross-section of a muscle fiber. Scale bar = 500 nm. (b) Longitudinal section of a muscle fiber. Scale bar = 2 μm. (c) Cross-section of a muscle fiber. Normal mitochondria are located in the subsarcolemmal lesion. Scale bar = 2 μm. (d) Mitochondria and vacuolar structures in a necrotising fiber. Scale bar = 2 μm. (e) Longitudinal section of a muscle fiber. Scale bar = 2 μm. (f) Vacuolar structure in a non-necrotising fiber. Arrows indicate a vacuolar structure. Scale bar = 500 nm. Con indicates Rpt3f/f mice, and mKO indicates muscle-specific Rpt3-knockout mice (ACTA1-rtTA;tetO-Cre;Rpt3f/f).