Fig. 1. The let1 mutants suppress autoimmunity triggered by silencing MEKK1.
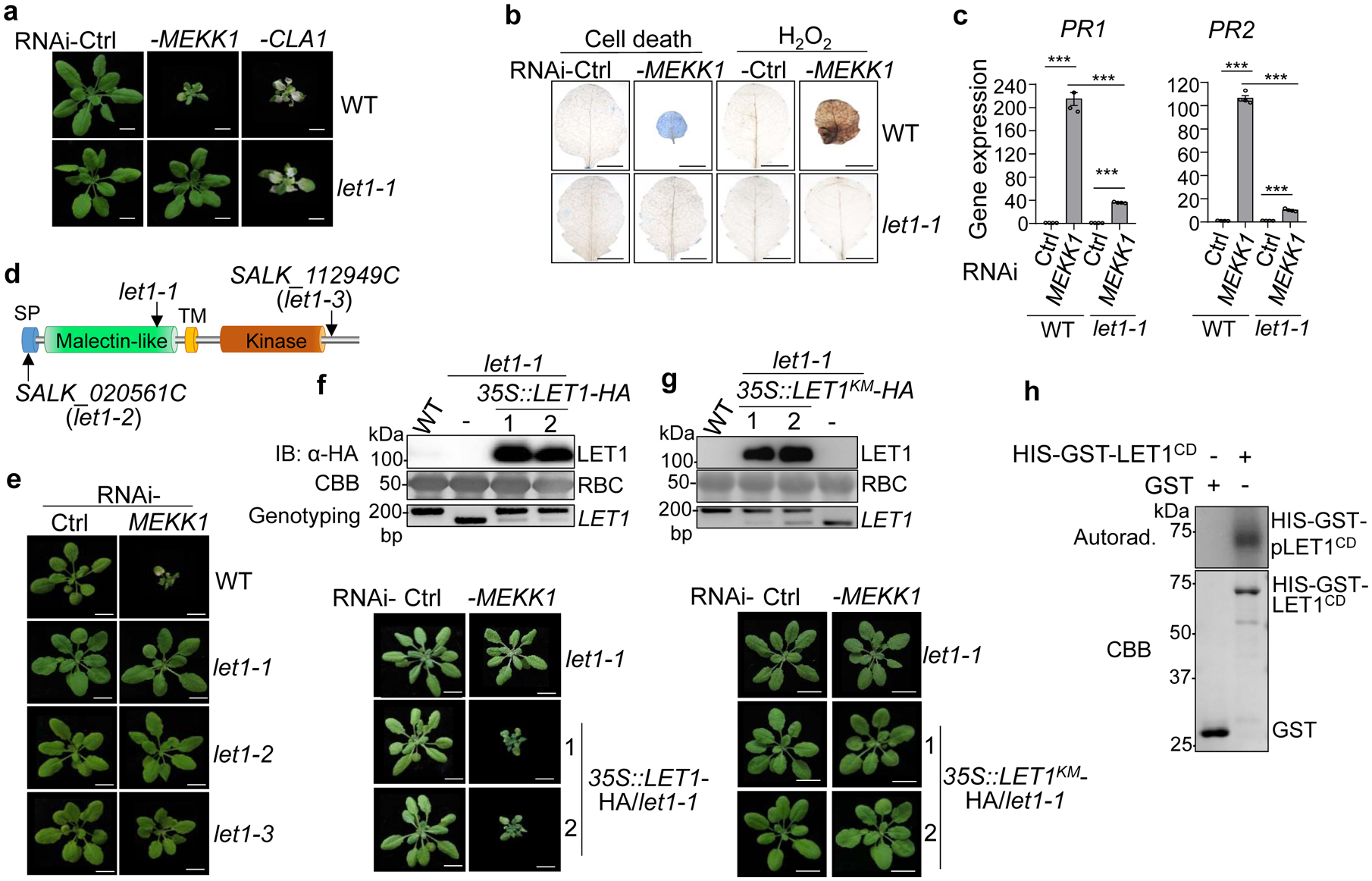
a, The let1–1 mutant suppresses growth defects triggered by RNAi-MEKK1. Plants of WT and let1–1 are shown three weeks after the inoculation of Agrobacterium carrying the VIGS vector control (Ctrl), VIGS-MEKK1, or VIGS-CLA1. Plant dwarfism and leaf chlorosis after silencing MEKK1 were observed in WT but not in let1–1. The albino phenotype of WT and let1–1 after silencing CLA1 (Cloroplastos alterados 1) was used as a visible indicator for VIGS efficiency. Scale bar, 1 cm.
b, The let1–1 mutant suppresses cell death and H2O2 production triggered by RNAi-MEKK1. True leaves after VIGS of MEKK1 were stained with trypan blue for cell death and DAB for H2O2 accumulation. Scale bar, 0.5 cm.
c, The let1–1 mutant suppresses PR1 and PR2 expression triggered by RNAi-MEKK1. The expression of PR1 and PR2 was normalized by the expression of UBQ10. P = 1.42 × 10−6 (PR1, column 1 and 2), P = 6.06 × 10−10 (PR1, column 3 and 4), P = 4.09 × 10−6 (PR1, column 2 and 4), P = 7.28 × 10−9 (PR2, column 1 and 2), P = 3.73 × 10−6 (PR2, column 3 and 4), P = 1.48 × 10−8 (PR2, column 2 and 4). Data are shown as mean ± SE from four independent repeats. The asterisks indicate statistical significance by using two-sided two-tailed Student’s t-test (***, P < 0.001).
d, The schematic diagram of LET1 protein motifs consisting of the signal peptide (SP), malectin-like domain, transmembrane domain (TM) and kinase domain. Arrows indicate T-DNA insertion sites or deletion sites of the different mutant alleles of let1.
e, The let1–2 and let1–3 mutants suppress growth defects triggered by RNAi-MEKK1. Experiments were done similarly as in a.
f, Complementation of the let1–1 mutant with LET1 restores the growth defects by RNAi-MEKK1. #1 and #2 are two homozygous complementation lines carrying 35S::LET1-HA in the let1–1 mutant background. Scale bar, 1 cm. The immunoblot by an α-HA antibody shows LET1-HA proteins (top panel); Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) staining of Rubisco proteins (RBC) serves as a loading control (middle panel), and genotyping PCR using primer pairs spanning the deletion site in let1–1 was used to confirm the deletion in let1–1 (bottom panel).
g, LET1KM cannot complement the let1–1 mutant for the growth defects by RNAi-MEKK1. #1 and #2 are two homozygous complementation lines carrying 35S::LET1KM-HA in the let1–1 mutant background. Experiments were done similarly as in f.
h, LET1 bears kinase activity. The LET1 cytosolic kinase domain fused with HIS-GST (HIS-GST-LET1CD) was expressed in insect cells. The kinase assay was performed using purified GST or HIS-GST-LET1CD proteins with [γ−32P] ATP (top panel). The CBB staining of input proteins is shown on the bottom panel.
The experiments in a-g were repeated at least three times, and h was repeated twice with similar results.
