Fig. 4.
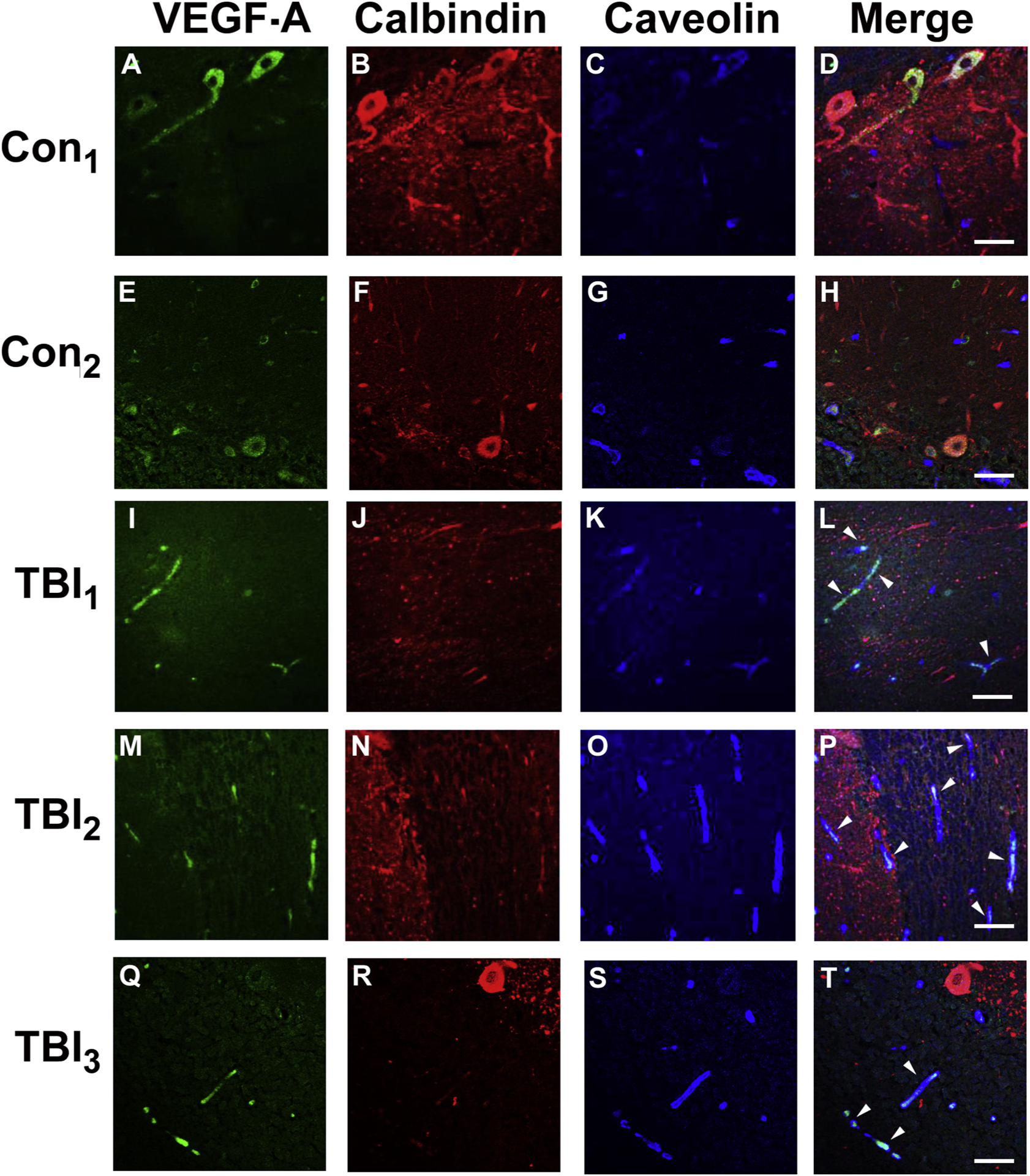
VEGF-A accumulates in cerebellum of veterans with blast-related mTBI.
Cerebellar postmortem specimens from veterans and active duty servicemembers with blast-related (TBI1–3) and two controls with no known TBI history (see Results, 3.5) were immunostained for VEGF-A (green), calbindin (red) that stains Purkinje cell bodies/processes, and caveolin (blue), which stains vascular endothelial cells. In distinction to controls (A-H), in the TBI cases (I-T), VEGF-A immunostaining was associated with microvascular profiles (caveolin-positive) (white arrow heads). In keeping with previous findings [52], prominent Purkinje cell body VEGF-A expression was observed, thereby supporting the specificity of the VEGF-A immunostaining, but did not reliably distinguish the mTBI and control cases. Scale bars = 50 μm.
