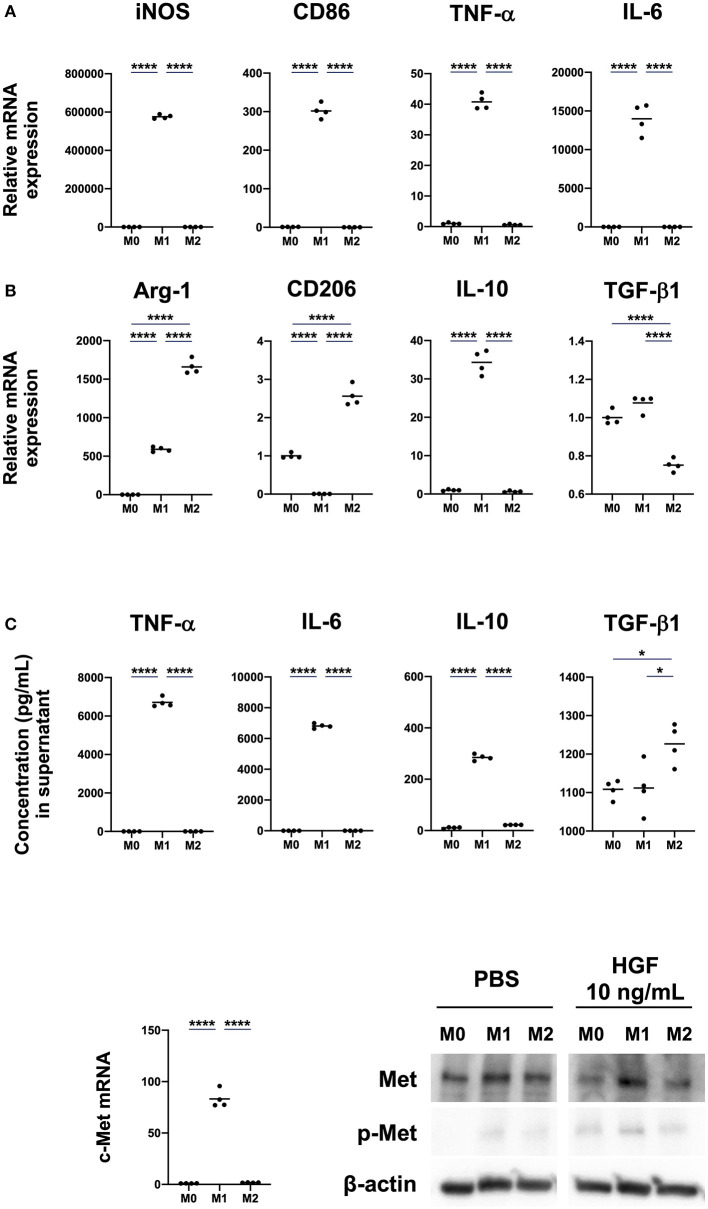
Figure 1.
M1 macrophages induced by IFN-γ and LPS treatment show enhanced expression and phosphorylation of c-Met. (A) Expression of M1 and M2 markers. Bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs; M0 macrophages) were differentiated by treatment of bone-marrow cells with M-CSF (25 ng/mL) for 7 days. Macrophages were polarized to M1 and M2 phenotypes by treatment for 48 h with IFN-γ and LPS or IL-4, respectively. Total RNA extraction and RT-qPCR were used to analyze mRNA expression of the M1 markers iNOS, CD86, TNF-α, and IL-6 and M2 markers Arg-1, CD206, IL-10, and TGF-β1. (B) Concentrations of cytokines in cell culture supernatant. ELISA was used to measure spontaneous secretion of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10, and TGF-β1 in cell culture supernatant from M0, M1, and M2 macrophages. (C) Expression of c-Met in M0, M1, and M2 macrophages. c-Met expression was compared using RT-qPCR and western blot. The RT-qPCR Ct values were normalized to those of β-actin and have been expressed relative to mean level in M0, which is arbitrarily defined as 1. β-actin was used as a loading control for western blots. The results are represented as the mean and a scatter plot of individual data points (n = 4). One-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05 and ****P < 0.0001.