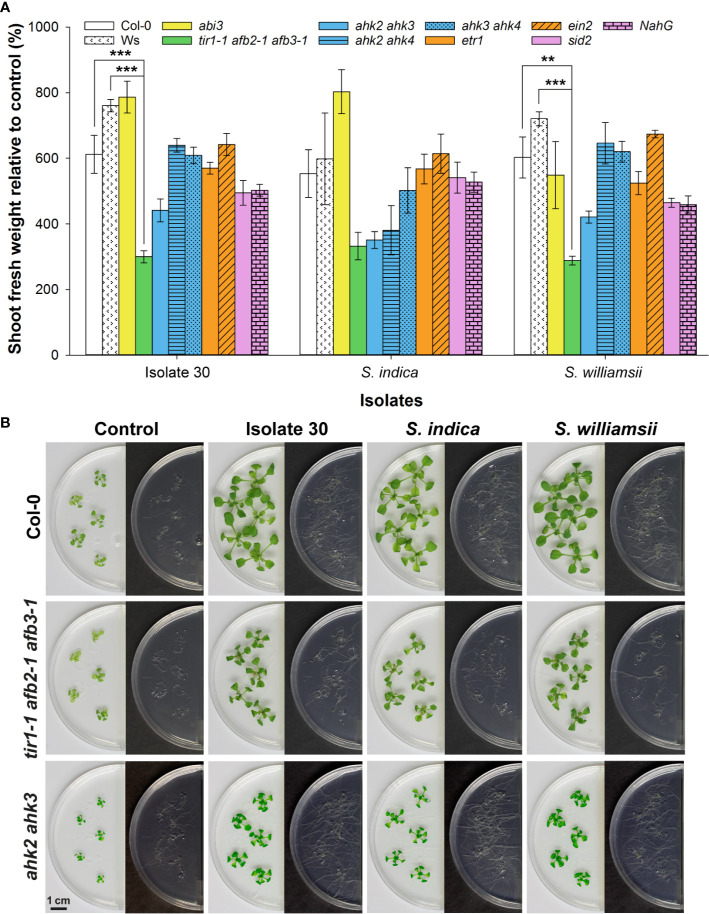
Figure 8.
Split-plate assay with Arabidopsis hormone-related mutants to explore the mechanisms underlying Serendipita VOC-mediated growth promotion. (A) Average shoot fresh weight of Arabidopsis wild‐type and mutant plants grown on ½ MS without sucrose after being exposed for 10 days to volatiles of isolate 30, S. indica and S. williamsii cultured on PDA, expressed relative to the corresponding untreated control. The bar color indicates the hormone type studied: white = wild type (Col-0 and Ws), yellow = abscisic acid (abi3), green = auxin (tir1-1 afb2-1 afb3-1), blue = cytokinin (ahk2 ahk3, ahk2 ahk4 and ahk3 ahk4), orange = ethylene (etr1 and ein2), purple = salicylic acid (sid2 and NahG). All lines are derived from the Col-0 ecotype, except for tir1-1 afb2-1 afb3-1, which has a mixed Col-0 (tir1-1)/Ws (afb2-1 afb3-1) background. Error bars represent standard errors on the mean of three biological replicates with each replicate consisting of five plants. For each of the three isolates tested, the magnitude of the growth response in the mutant lines was compared with that in the corresponding wild type by performing a Dunnett’s test; asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (** < 0.01, *** < 0.001). (B) Shoot and root growth in the Col-0 wild type and the two least responsive mutant lines after 10 days of co-cultivation with isolate 30, S. indica and S. williamsii. A complete overview showing the responses in all mutants is given in Supplementary Figure S18. Plates were sealed with Breathe-Easy strips.