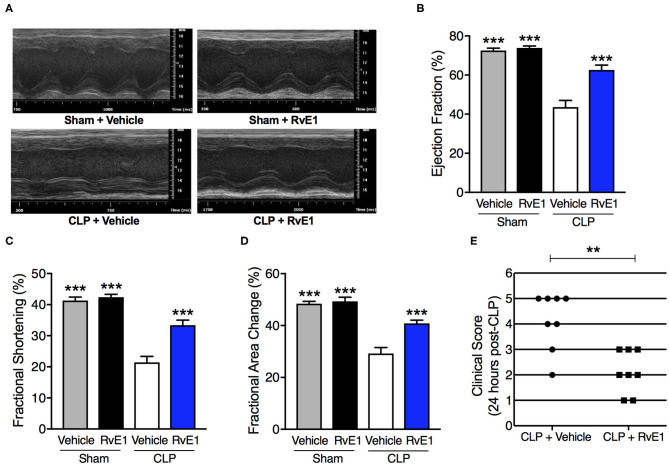
Figure 2.
One hour post-treatment of RvE1 attenuates CLP-induced cardiac dysfunction and sepsis-associated clinical scores in mice. Mice underwent sham or CLP surgery. One hour after CLP, mice were treated with either RvE1 (1 μg/mouse i.v.) or vehicle (100 μl PBS, 0.1% Ethanol). Cardiac function was assessed at 24 h. (A) Representative M–mode echocardiograms and percentages of (B) ejection fraction (C) fractional shortening, and (D) fractional area change. The following groups were studied: Sham + Vehicle (n = 6); Sham + RvE1 (n = 6); CLP + Vehicle (n = 8) and CLP + RvE1 (n = 8). All data are represented as means ± SEM. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test. ***P < 0.001 vs. CLP + Vehicle group. (E) At 24 h post-CLP, mice were scored for the presence or absence of six different macroscopic signs of sepsis, namely, lethargy, piloerection, tremors, periorbital exudates, respiratory distress, and diarrhea. A clinical score >3 is considered as severe sepsis. Data are from 16 mice and were analyzed by unpaired Student's t-test. **P < 0.01 vs. CLP + Vehicle group.