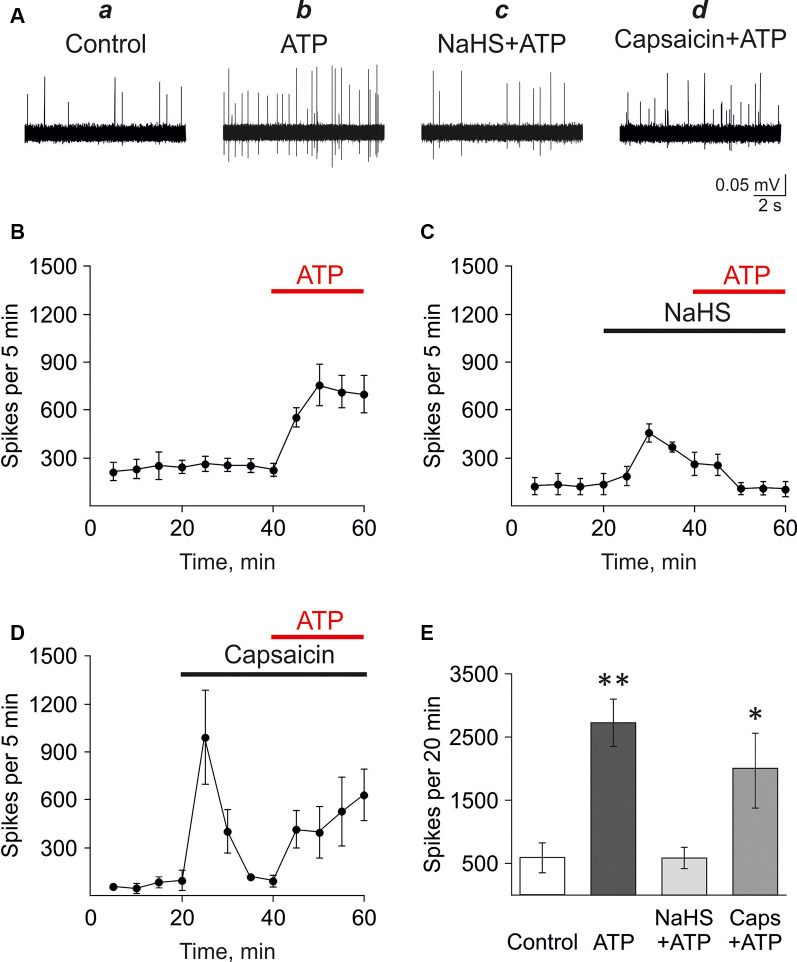
Figure 1.
Testing the action of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) on the pro-nociceptive effect of ATP in trigeminal afferents. (A) Example traces of action potentials in the trigeminal nerve in control (a), with ATP application (100 μM; b), ATP plus NaHS application after preincubation in NaHS (100 μM; c), ATP plus capsaicin application after preincubation in capsaicin (1 μM; d). (B) The frequency of action potentials during application of ATP (n = 5). (C) The frequency of action potentials during application of ATP (100 μM) in the presence of NaHS after preincubation with NaHS (100 μM; n = 4). (D) The frequency of action potentials during the application of ATP (100 μM) in the presence of capsaicin after preincubation with capsaicin (1 μM; n = 4). (E) The histograms showing the frequency of action potentials per 20 min in the trigeminal nerve in control and after application of ATP (100 μM), α,β-meATP (20 μM), in control and in the presence of NaHS or capsaicin. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.