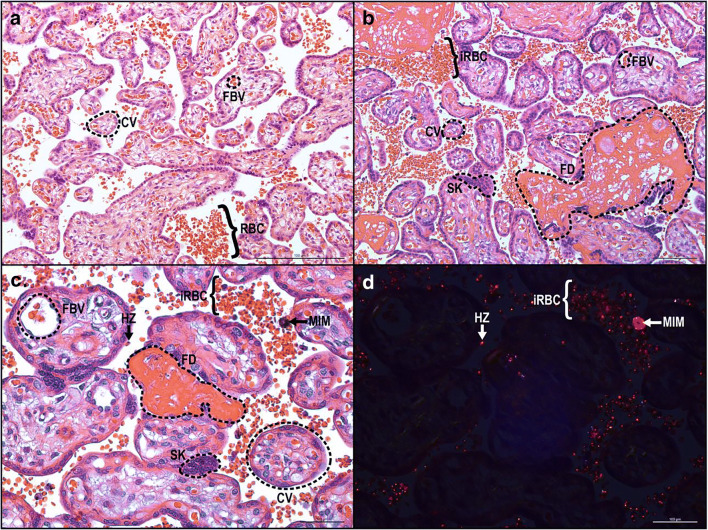
Fig. 2.
Histological cross section of chorionic villi. (a) Chorionic villi (CV) have a continuous layer of syncytiotrophoblasts separating fetal and maternal cells. Fetal blood vessels (FBV) are located within the CV whereas maternal red blood cells (RBC) are circulating in the intervillous space (IVS). (b) During placental malaria, infected red blood cells (iRBC) accumulate within the IVS and lead to fibrin deposition (FD) and syncytial knot (SK) formation. Normal light (c) and polarized light (d) microscopy of malaria-infected placenta demonstrating hemozoin (HZ), dark-brown pigment in normal light and red in polarized light, accumulation within iRBC, and maternal intervillous monocyte (MIM)