Fig. 4.
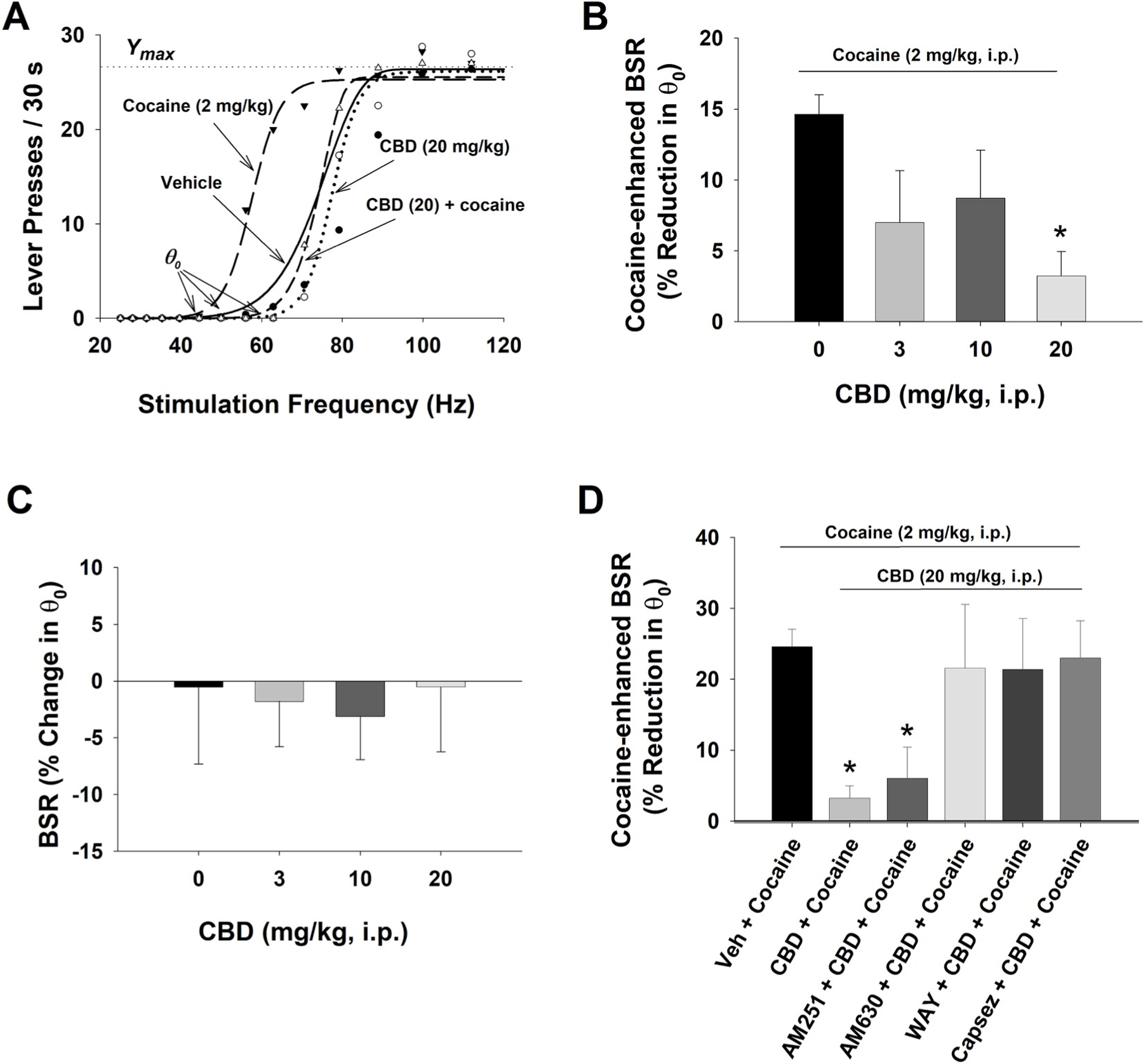
The effects of CBD on electrical brain-stimulation reward (BSR). A. Representative rate-frequency function curves for BSR, illustrating the BSR threshold θ0, Ymax, and the effects of cocaine and/or CBD on BSR. Cocaine, at 2 mg/kg (i.p.) shifted the rate-frequency function curve to the left, lowering the θ0 value (i.e., enhancing BSR), without a change in the Ymax level. Pretreatment with CBD (20 mg/kg) blocked cocaine-enhanced effect. B: Percent changes in the θ0 value, indicating that cocaine significantly enhanced BSR, which was dose-dependently attenuated by CBD treatment. n = 11 in each dose group. C: CBD alone, at the doses of 3, 10, 20 mg/kg, failed to alter BSR. n = 8 in each dose group. D: Pretreatment with AM630 (n = 9), WAY100135 (n = 7) or capsazepine (n = 7), but not AM251 (n = 7), blocked CBD-induced reduction in cocaine-enhanced BSR. *p < 0.05, compared to the (Veh + Cocaine) group.
