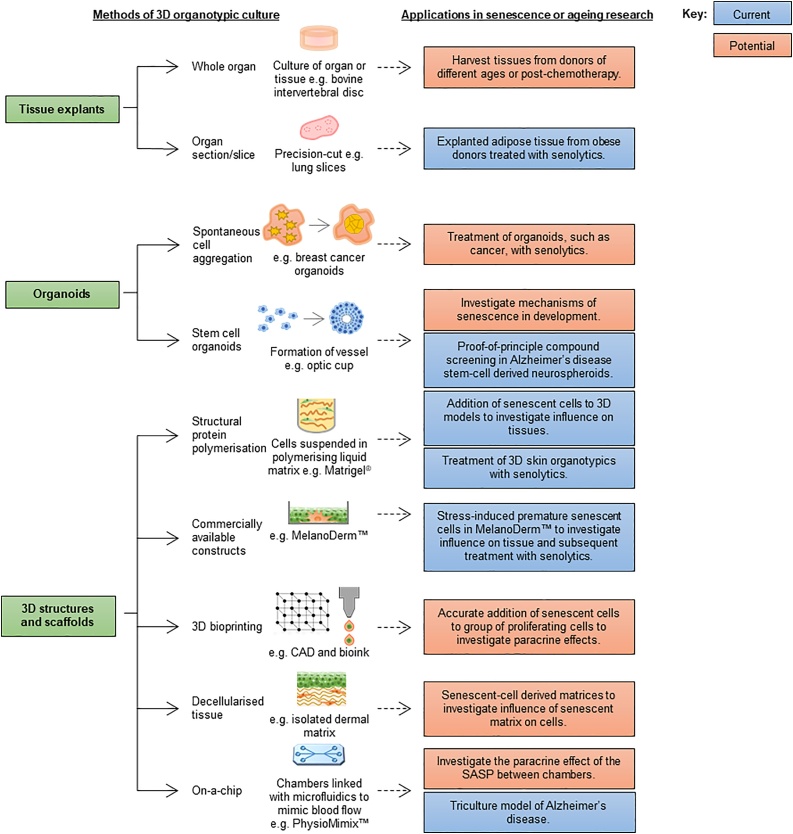
Fig. 1.
Overview of current methodologies of 3D organotypic culture and future applications for organotypics in senescence research. Methods of organotypic culture are divided into 3 categories (left): tissue explants, organoids and 3D structures and scaffolds. Tissue explants include the use of whole organ culture and organ sections or slices. Organoids can be sub-divided into spontaneously forming aggregates or inducible stem cell organoids. Finally, 3D structures include the use of structural protein polymerisation, commercially available constructs, models built using 3D bioprinting techniques, decellularised human or animal model tissue and ‘on-a-chip’ assays. Examples of current applications of these techniques are shown in blue, whereas opportunities for future applications are shown in orange.