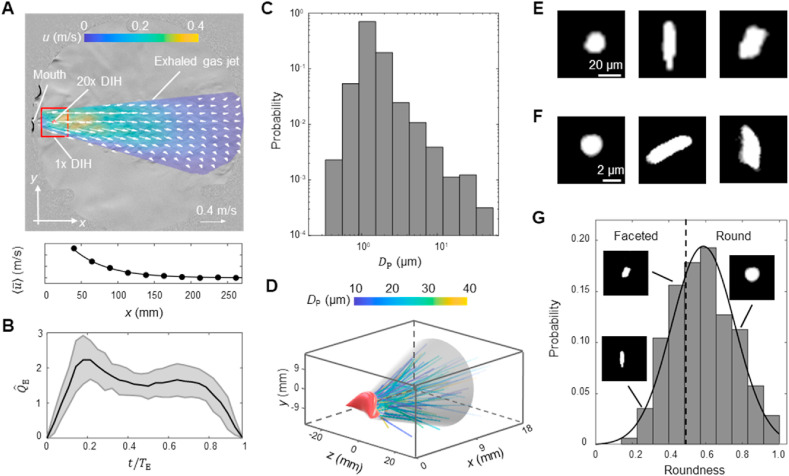
Fig. 1.
(A) The ensemble average flow field of exhaled gas of all participants superimposed onto an enhanced Schlieren image sample of exhaled gas flow. The details of generating this figure can be found in the supplementary materials. The locations of the mouth, the sampling windows of 1X and 20X digital inline holography (DIH) are marked in the figure. Additionally, the streamwise velocity averaged over the cross section of the exhalation cone () is plotted against the streamwise distance to the mouth (x) to show the decay of flow velocity. (B) The change of the normalized exhaled gas flow rate () in one exhalation cycle of time period , where is the instantaneous exhaled gas flow rate ( divided by its average for each exhalation cycle. The solid curve and shaded area represent the ensemble average and variance of of all participants, respectively. (C) The histogram of particle size quantified using area equivalent diameter (). (D) The 3D trajectories of all the particles captured using 1X magnification DIH. Sample images of particles from (E) 1X and (F) 20X DIH measurements. (G) The histogram of particle shape quantified using particle roundness (Fig. S7 with details in the supplementary materials) with inset figures showing samples of particles with different roundness levels. The solid line is the fitted normal distribution and the dashed line corresponds to the roundness of 0.5.