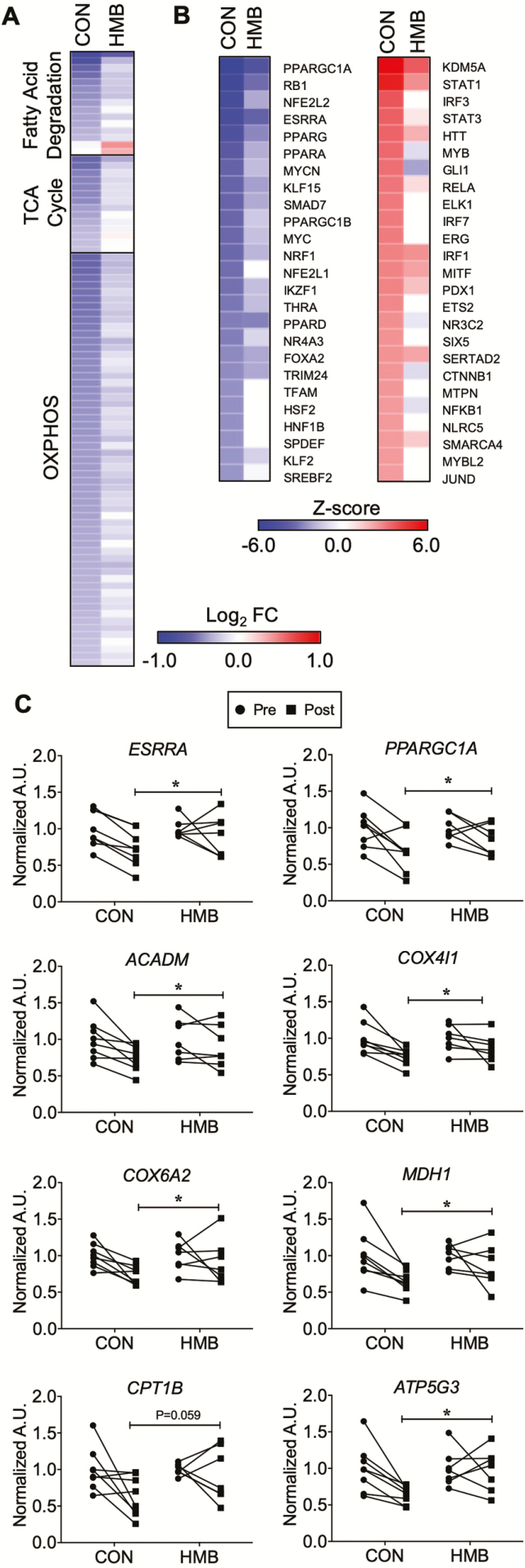
Figure 3.
Gene regulatory networks involved in skeletal muscle oxidative metabolism are down-regulated following 10 days of bed rest (BR). (A) The heat map represents the log2 fold change of all transcripts in the indicated KEGG pathway that are significantly regulated (p < .05) during BR in either the CON or β-hydroxy-β-methylbuturate (HMB) groups. (B) IPA Upstream Regulator Analysis was used to identify transcription regulators and ligand activated transcription factors significantly regulated (Z-score >2 or <−2) in either CON or HMB groups. The heat map represents the Z-score for the top 25 inhibited (left) or activated (right) factors in the CON group and the corresponding Z-score in the HMB group. n = 5 per group for transcriptomic analysis. OXPHOS = oxidative phosphorylation. (C) RT-qPCR assay for expression of key nuclear transcription factors, and genes involved in fuel metabolism pre- and post- 10 days of BR. n = 7–8 per group. * Significant time effect for reductions following BR: ERRα (ESRRA) (Time Effect: p = .01, Interaction: p = .19), PGC1-α (PPARGC1A) (Time Effect: p = .003, Interaction: p = .25), MCAD (ACADM) (Time Effect: p = .001, Interaction: p = .19), COX4I1 (COX4I1) (Time Effect: p = .002, Interaction: p = .30), COX6A2 (COX6A2) (Time Effect: p = .03, Interaction: p = .23), ATP synthase (ATP5G3) (Time Effect: p = .03, Interaction: p = .06) and MDH1 (MDH1) (Time Effect: p = .005, Interaction: p = .19). † trend for time effect for CPT1 (CPT1B) (Time Effect: p = .058, Interaction: p = .20) to be reduced following BR.