Fig 2. Early and late efficacy of single dose PEP regimens against M. leprae.
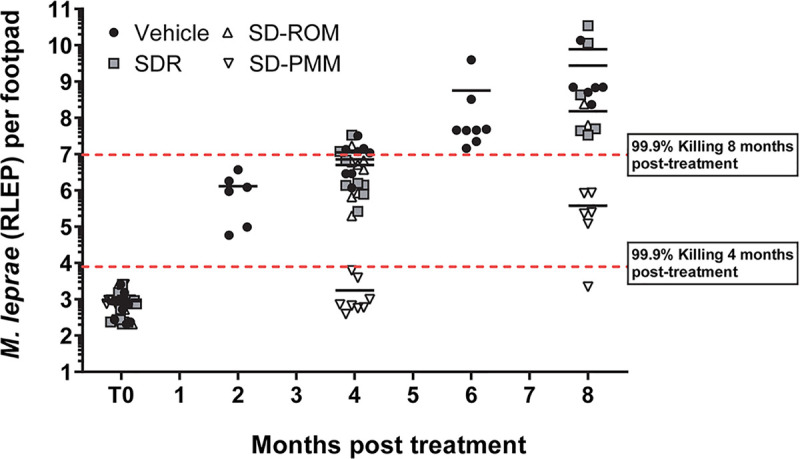
Athymic nude mice were infected in both hind footpads with 6 x103 M. leprae. Mice were treated with single dose rifampin (SDR), single dose ROM (rifampin, ofloxacin, minocycline), or single dose PMM (rifapentine, moxifloxacin, minocycline). M. leprae were enumerated by RLEP qPCR at two, four, six, and eight months post treatment. Bars represent the mean for each group. A regression analysis was calculated to determine the expected RLEP value if 99.9% of the bacilli were killed after the administration of the single dose regimen (r2 = 0.933). The 99.9% kill line at 4 months was 7.94 x 103 bacilli, and the 99.9% kill line at 8 months was 9.55 x 106 bacilli.
