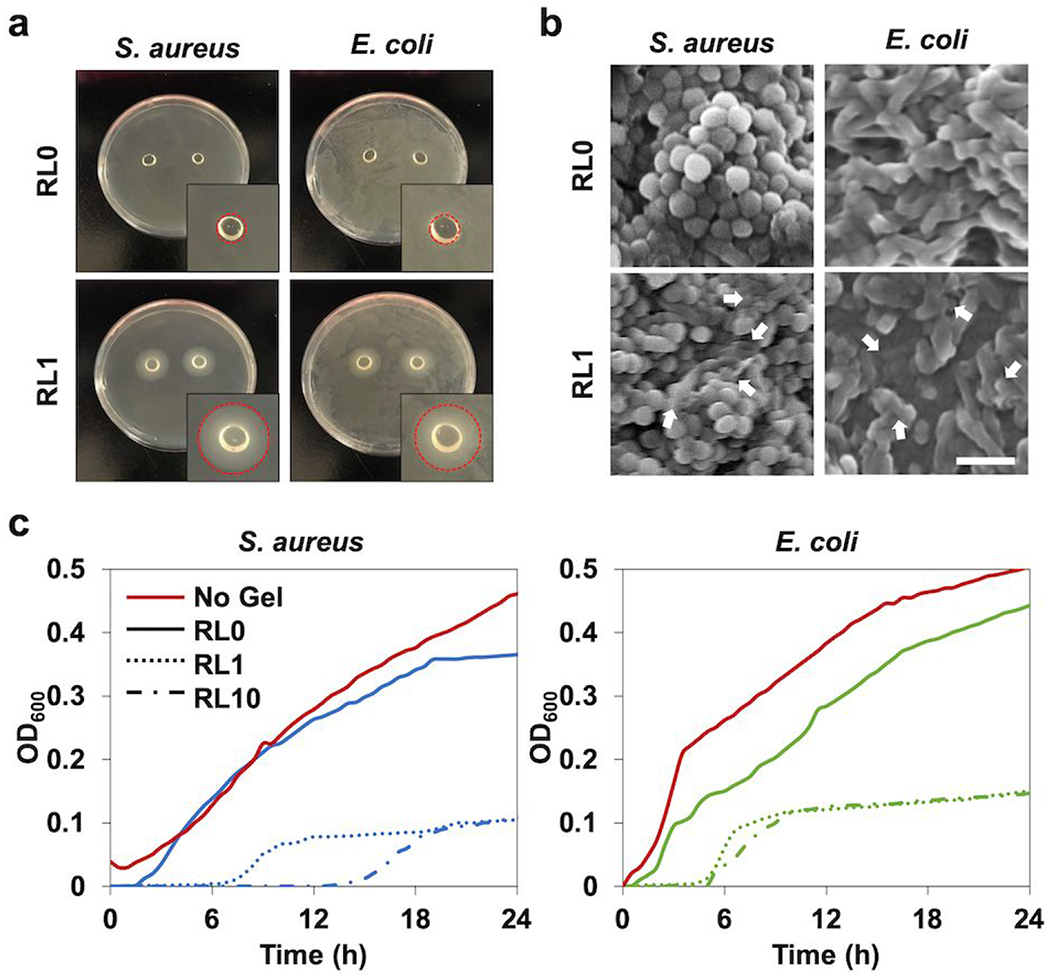
Figure 7.
In vitro antibacterial characterization of lysozyme incorporated hydrogels, (a) Agar petri dish cultured with S. aureus and E. coli with hydrogel samples placed on the center of the dish for one day to analyze inhibition zone. Circle areas of inset indicate the inhibition zone, (b) SEM micrographs of S. aureus and E. coli in the hydrogels following one day incubation. The white arrows indicate the damaged bacterial membranes or intracellular efflux after contact with the hydrogel modified with lysozyme. Scale bar is 2 μm. (c) Antibacterial activity of the hydrogels with different lysozyme concentrations (RL0, RL1, RL10) to S. aureus and E. coli over 24h tested by microplate proliferation assay.