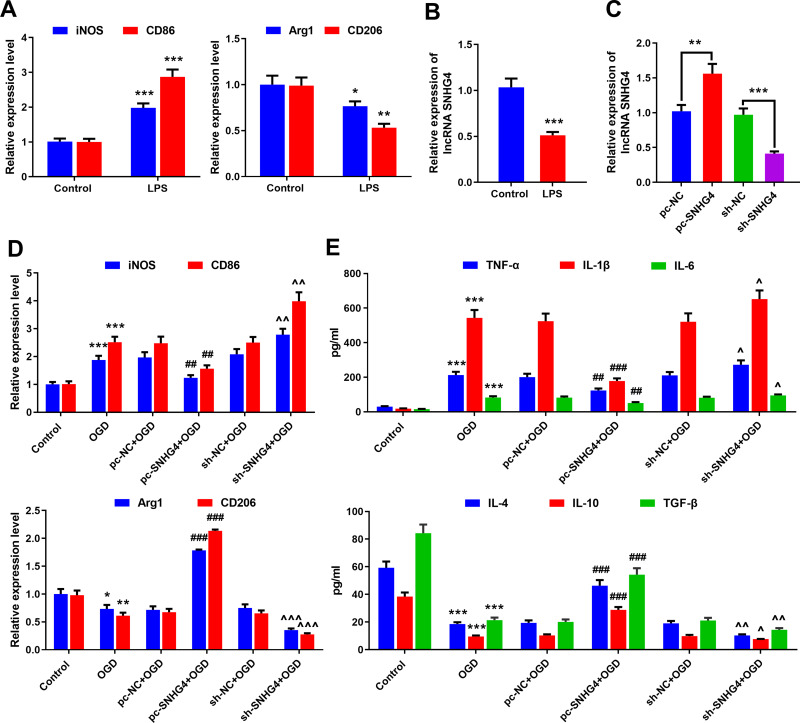
Figure 2.
SNHG4 overexpression inhibits microglial activation and inflammatory responses. (A) qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of M1 markers iNOS and CD86 and M2 markers Arg1 and CD206 in microglia treated with LPS; (B) qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of SNHG4 in microglia treated with LPS; (C) qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of SNHG4 cell models with SNHG4 overexpression and knockdown; (D) qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of M1 markers iNOS and CD86 and M2 Arg1 and CD206 in microglia treated with OGD. (E) ELISA was used to detect the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 β, IL-6, TNF- α) and anti-inflammatory factors (IL-4, IL-10, TGF-β). *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, and ***P< 0.001 versus the control group; ##P< 0.01 and ###P< 0.001 versus the pc-NC+OGD group; ^P< 0.05, ^^ P< 0.01 and ^^^P< 0.001 versus the sh-NC+OGD group.
Abbreviations: iNOS, induced nitric oxide synthase; CD, cluster of differentiation; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; OGD, oxygen-glucose deprivation; pc, pc-DNA3.1; NC, negative control; sh, short-hairpin RNA; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; IL, interleukin; TGF, transforming growth factor.