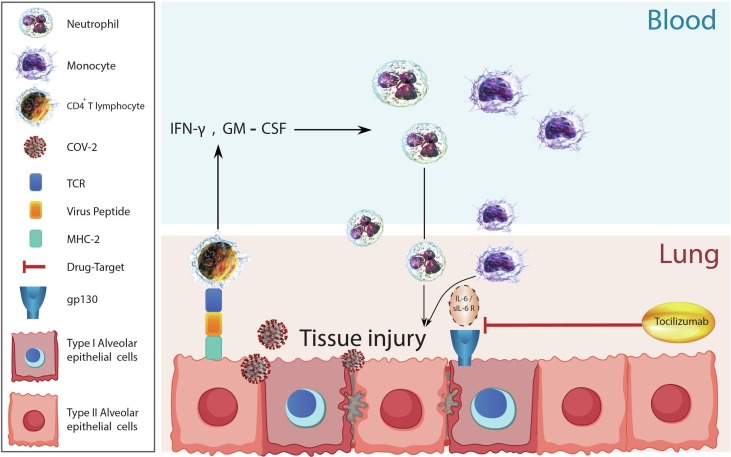
Fig. 1.
Possible mechanism of lung tissue injury by Covid-2. Virus particles become phagocytosis by alveolar cells. These cells present the virus peptides through MHC-II to CD4+ T lymphocytes. CD4+ T lymphocytes activate and produce IFN-γ, GM-CSF and other inflammatory cytokines. These inflammatory cytokines recruit blood leukocytes such as neutrophils and monocytes into inflamed lung tissue. Neutrophils and monocytes activate and produce reactive oxygen species (not shown in the figure) and IL-6. IL-6 bind to sIL-6-R that form an IL-6/ sIL-6R complex. This complex bind to alveolar epithelial cells through gp130 and during the hierarchy happen tissue injury. Tocilizumab neuralizes binding of IL-6/ sIL-6R to alveolar epithelial cells. GM-CSF: granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, gp: glycoprotein, IFN: interferon, IL: interleukin and MHC: major histocompatibility complex, sIL-6-R: soluble IL-6 receptor.