Fig. 1. HF intake–affected pathways and genes in hearts using RNA-seq and effect of obesity on mitophagy markers in the heart.
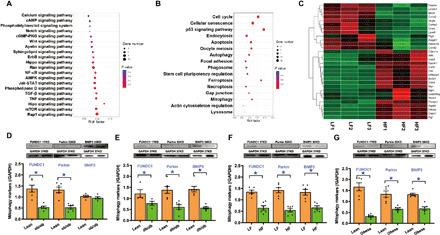
(A to C) Rats were fed HF (60% fat) diet for 20 weeks, and cardiac tissues were collected and subjected to RNA-seq. (A) Signal transduction pathway of KEGG. (B) Cellular processes of KEGG. (C) Heatmap displaying relative expression of autophagy and Ca2+ signaling pathway–related genes in the heart (n = 3). (D) Mitophagy protein profiles (FUNDC1, Parkin, and BNIP3) in adult ob/ob mouse hearts. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. (E) Mitophagy protein profiles in adult db/db mouse hearts. (F) Mitophagy protein profiles in adult rat hearts following 20 weeks of HF intake. (G) Mitophagy protein profiles in lean and obese human heart samples. Mean ± SEM; n = 4 to 6 group, *P < 0.05 between indicated groups.
