Fig. 2. Mechanism of IP6 binding to CA pentamers.
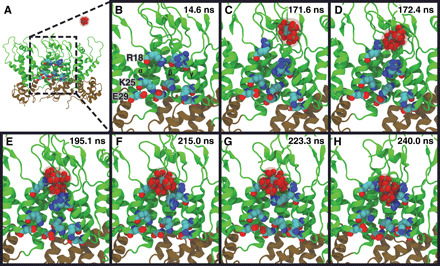
A series of snapshots from part of an MD trajectory show the chemical interactions involved in IP6 binding to the CA pentamer. Three CA domains are shown in a side view of the pentamer, with helix H1 of the CA domain labeled as α, β, and γ, respectively. Two additional CA domains (δ and ε) are not shown for clarity. The R18 ring and residues (K25-E29) that form a salt-bridge interaction proximal to the CTD are labeled. Time points are labeled in the upper-right corner of each panel. (A) The IP6 ligand is initially in bulk solvent. (B) Close-up view of the pore region in (A). (C) IP6 enters the pore past the β-hairpin of CA, and an arginine side chain flips away from the R18 ring. (D) The R18 side chain coordinates IP6. (E) IP6 is coordinated to multiple R18 side chains. (F) IP6 shifts toward the R18 ring. (G) IP6 reorients in the binding pocket. (H) IP6 is bound to the central arginine ring with R18 side chains contacting the negatively charged phosphates.
