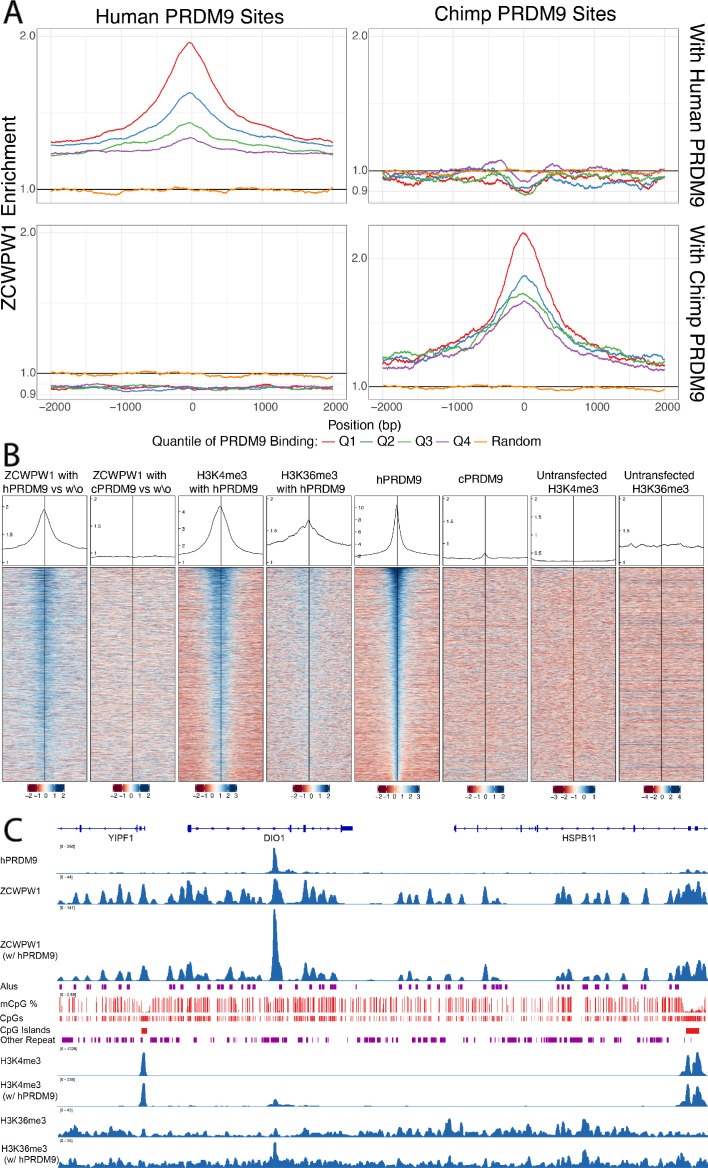
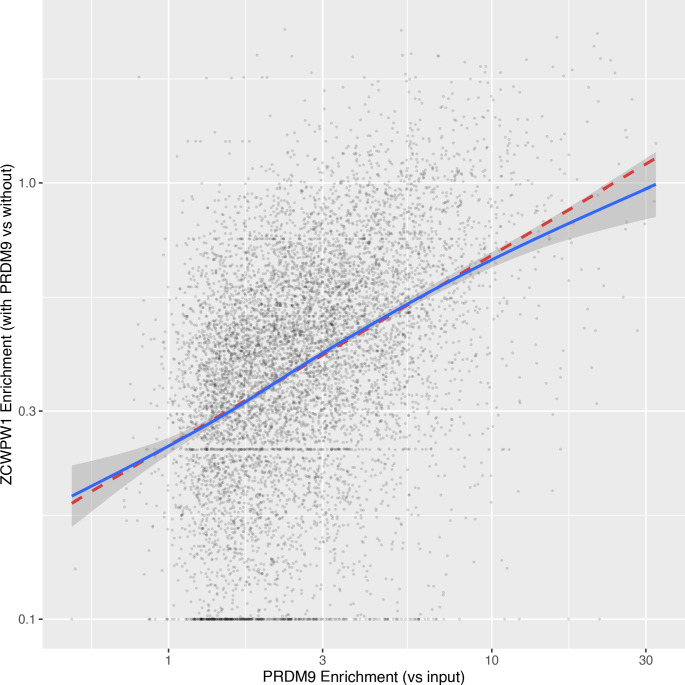
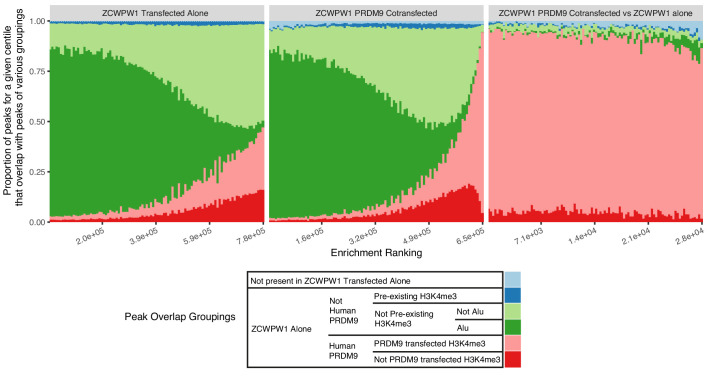
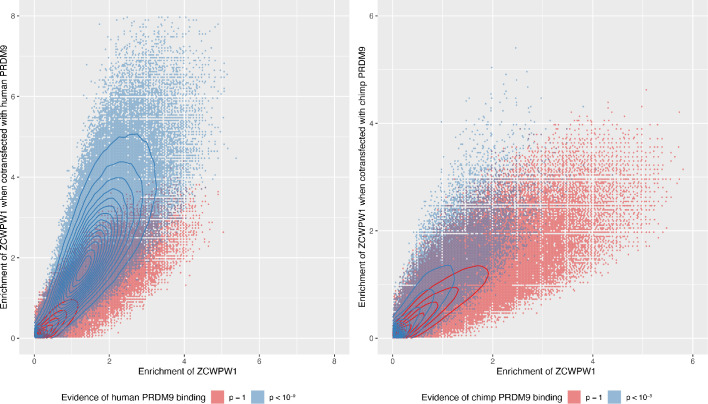
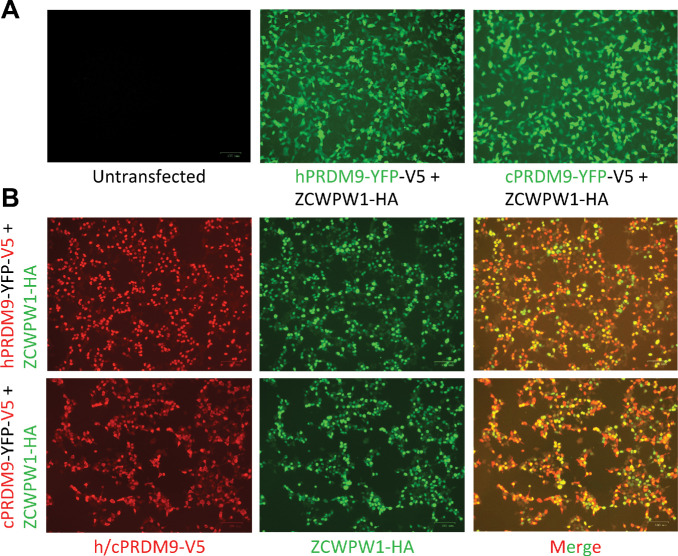
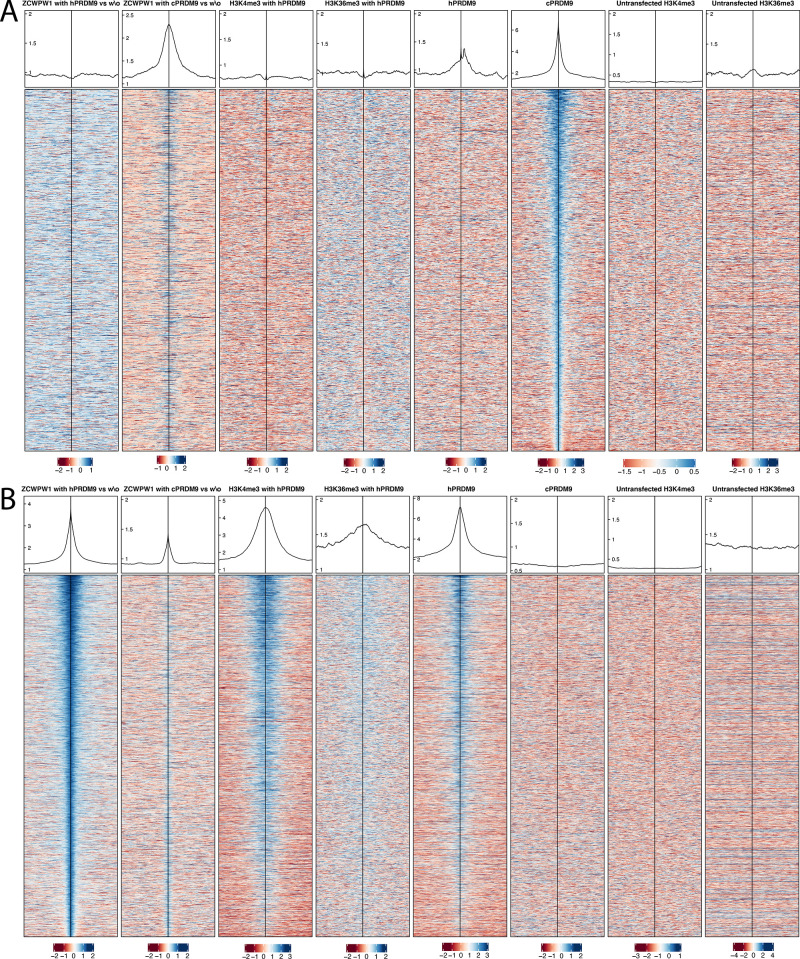
Figure 5. Enrichment and binding profiles of ZCWPW1 and other factors.
(A) Enrichment of ZCWPW1 (with vs without PRDM9) at PRDM9-binding sites when co-transfected with PRDM9 with either Human or Chimp Zinc Finger (Materials and methods section ‘Enrichment Profiles’). Q = quartile. Human PRDM9 sites are centered and stranded by the motif. Y-axis is log10 scale (y-axis labels remaining in linear space). (B) Profiles and heatmaps of reads from cells co-transfected with human (h) or chimp (c) PRDM9 around the top 25% of individual human PRDM9-binding sites (rows). Heatmaps: log-fold change of target (indicated in column titles, Materials and methods) vs input, for various labelled target proteins, ordered by human PRDM9. ZCWPW1, H3K4me3 and H3K36me3 each become enriched at human PRDM9 sites, following (co-)transfection with human PRDM9. Profiles: Sum of all target coverage divided by sum of all input coverage for all regions shown in the heatmap, shown on a linear scale. w\o, without. (C) ChIP-seq data and annotation in a genome plot illustrate the behaviour of ZCWPW1 and other factors. ChIP-seq tracks show fragment coverage. Tracks where PRDM9 is present are labeled ‘w/PRDM9’, and below, corresponding tracks without PRDM9. ZCWPW1 binds to Alus, CpG islands and other CpG-rich sequences even in the absence of PRDM9. On addition of PRDM9, ZCWPW1 becomes strongly enriched at PRDM9 binding locations (center left peak within DIO1). mCpG, methylated CpG.