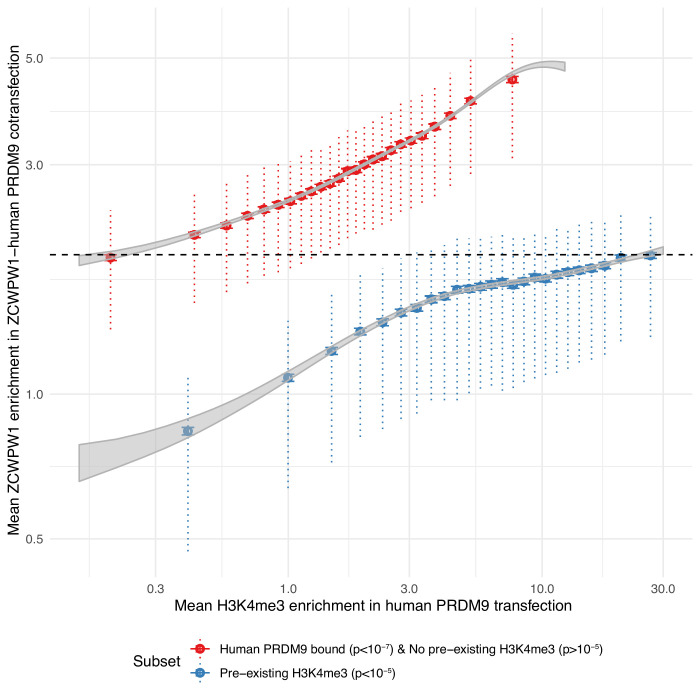
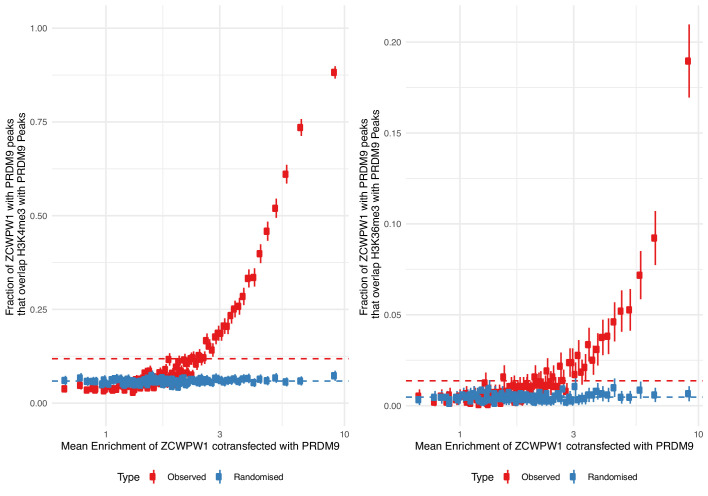
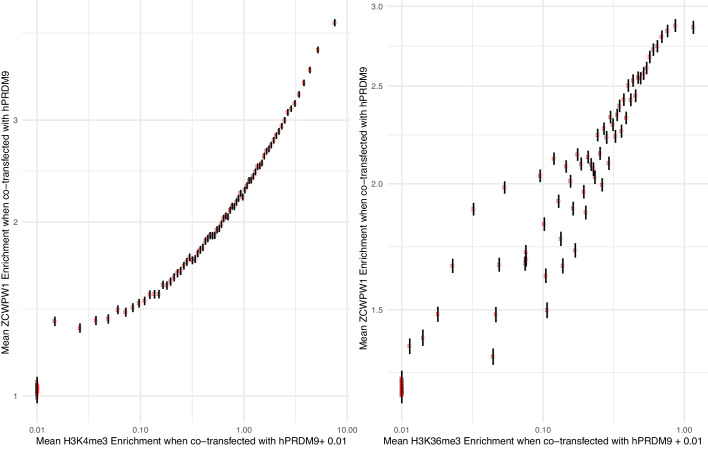
Figure 6. PRDM9-bound regions (H3K4me3 and H3K36me3) are a stronger recruiter of ZCWPW1 than promoters (H3K4me3 only).
For any given level of H3K4me3 (x-axis), ZCWPW1 enrichment (y-axis) is higher at PRDM9-bound regions (red) than regions with pre-existing H3K4me3 (promoters, blue). H3K4me3 and ZCWPW1 were force called in 100bp windows across all autosomes. These windows were split into two sets defined as indicated in the legend (where ‘p’ is the p-value from peak-calling required for a window to be included in the subset) with the additional constraint of requiring input fragment coverage >5 for ZCWPW1 and >15 for H3K4me3. p: p-value for non-zero level of input corrected coverage in that bin. ‘pre-existing H3K4me3’ refers to H3K4me3 that is present without transfection (of either PRDM9 or ZCWPW1), which is mainly found at promoter regions. For each subset, H3K4me3 was split into 25 bins with equal number of data points. Horizontal bars: two standard errors of the mean. Vertical dotted bars: upper and lower quartiles. Grey ribbons show two standard errors for a Generalized additive model on log(mean H3K4me3 enrichment + 0.1). Dashed black horizontal line highlights that the mean enrichment of the highest bin for promoters is similar to that of the lowest bin for PRDM9-bound sites.