Fig. 1. Consequences of abasic sites.
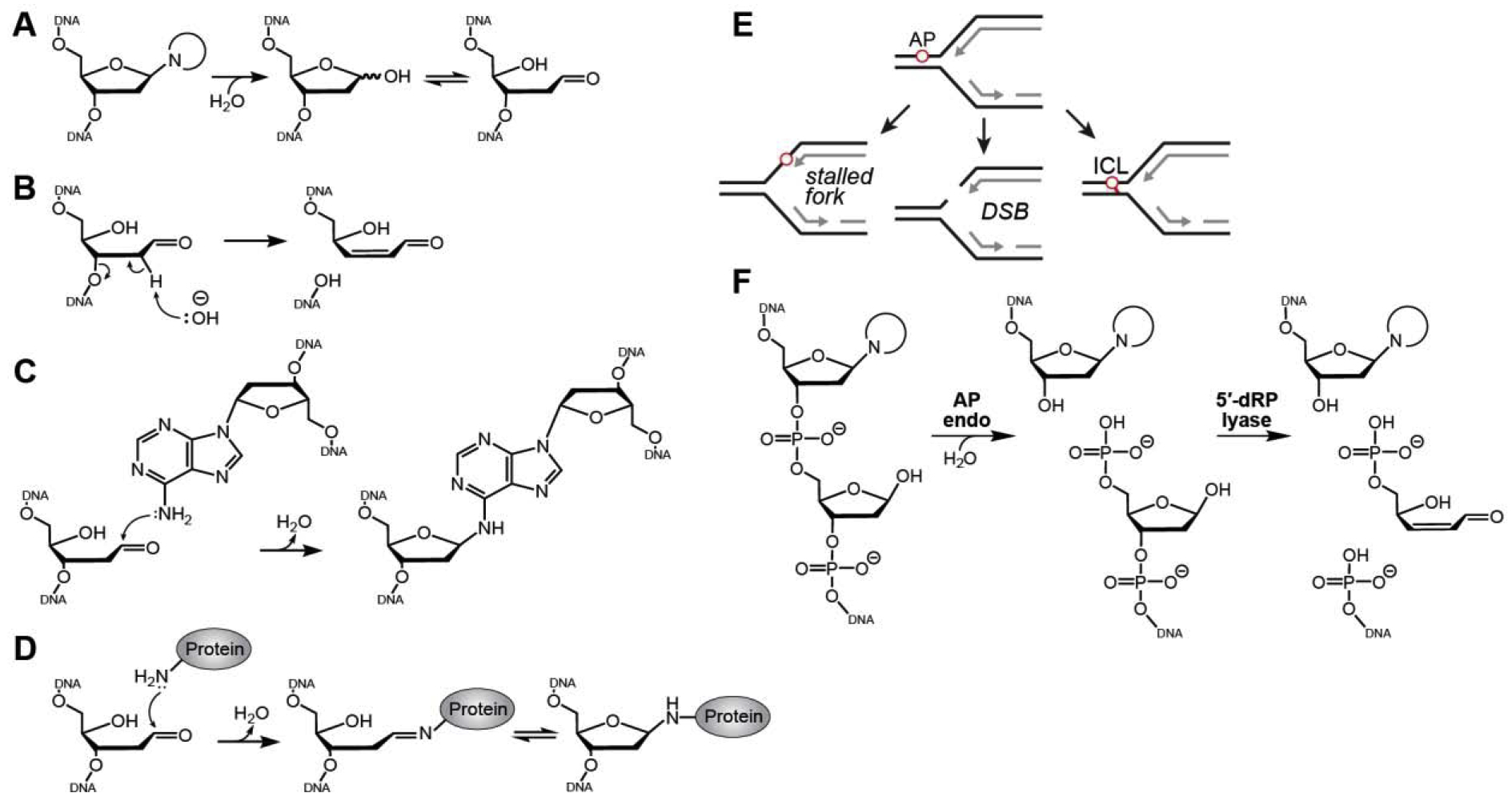
A. AP sites arise from enzymatic and spontaneous hydrolysis of the N-glycosidic bond and exist in either furanose or aldehyde forms. B. Base-catalyzed β-elimination of an AP site generates a strand break. C,D. Formation of an ICL (C) and a DPC (D) by nucleophilic attack of AP site C1ʹ by primary amines in DNA or proteins . E. Consequences of AP sites in the template strand during DNA replication. F. Incision of DNA by AP endonuclease and DNA lyases.
