Fig. 2. SRAP-DNA structure.
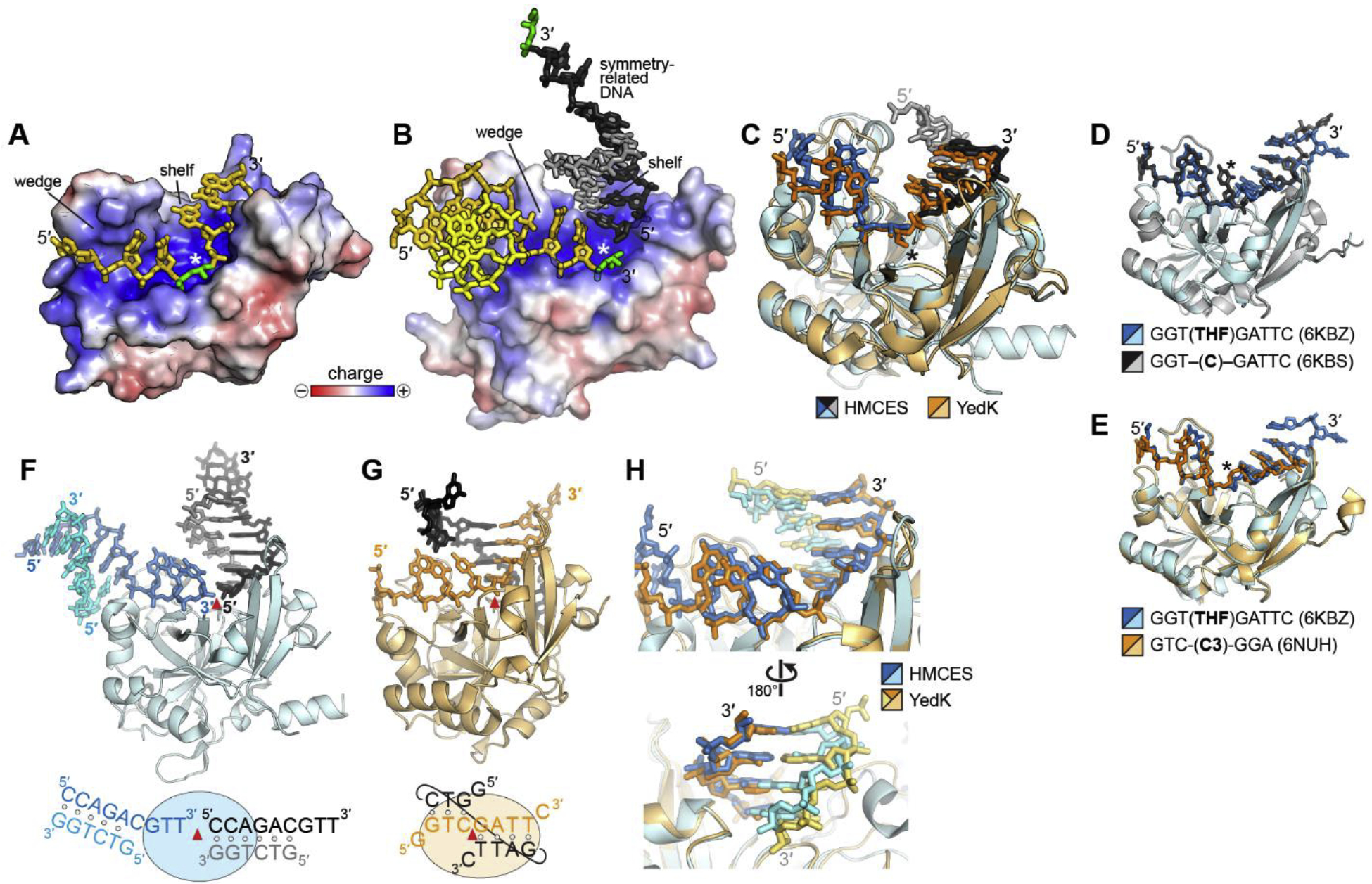
A,B. Electrostatic surface potential of (A) YedK-DPC (PDB ID 6NUA and (B) HMCES-SRAP DPC (PDB ID 6OE7) structures. The AP sites are green, and the symmetry-related DNA molecule in HMCES is shown in black and grey. The white asterisk denotes the position of the active site. C. Superposition of YedK-DPC (PDB ID 6NUA) and HMCES-SRAP DPC (PDB ID 6OE7). The DPC is marked with an asterisk. The ends of the DNA in the HMCES structure have been removed for clarity. D,E. Superposition of YedK bound noncovalently to ssDNA containing (D) a cytosine or an abasic site analog, and (E) two different abasic site analogs. The position of the nucleotide at the active site is marked with an asterisk. F,G. Similarity of dsDNA bound to (F) HMCES-SRAP (PDB ID 6OEB) and (G) YedK (PDB ID 6KBS). The asymmetric unit is colored blue or orange, and symmetry related DNA is shown in black and grey. The red triangle marks the position of the active site. In the schematic at the bottom, base pairs are denoted by open circles. H. Superposition of the two structures in panels F and G. DNA is colored blue/cyan in HMCES and orange/gold in YedK.
