Figure 1:
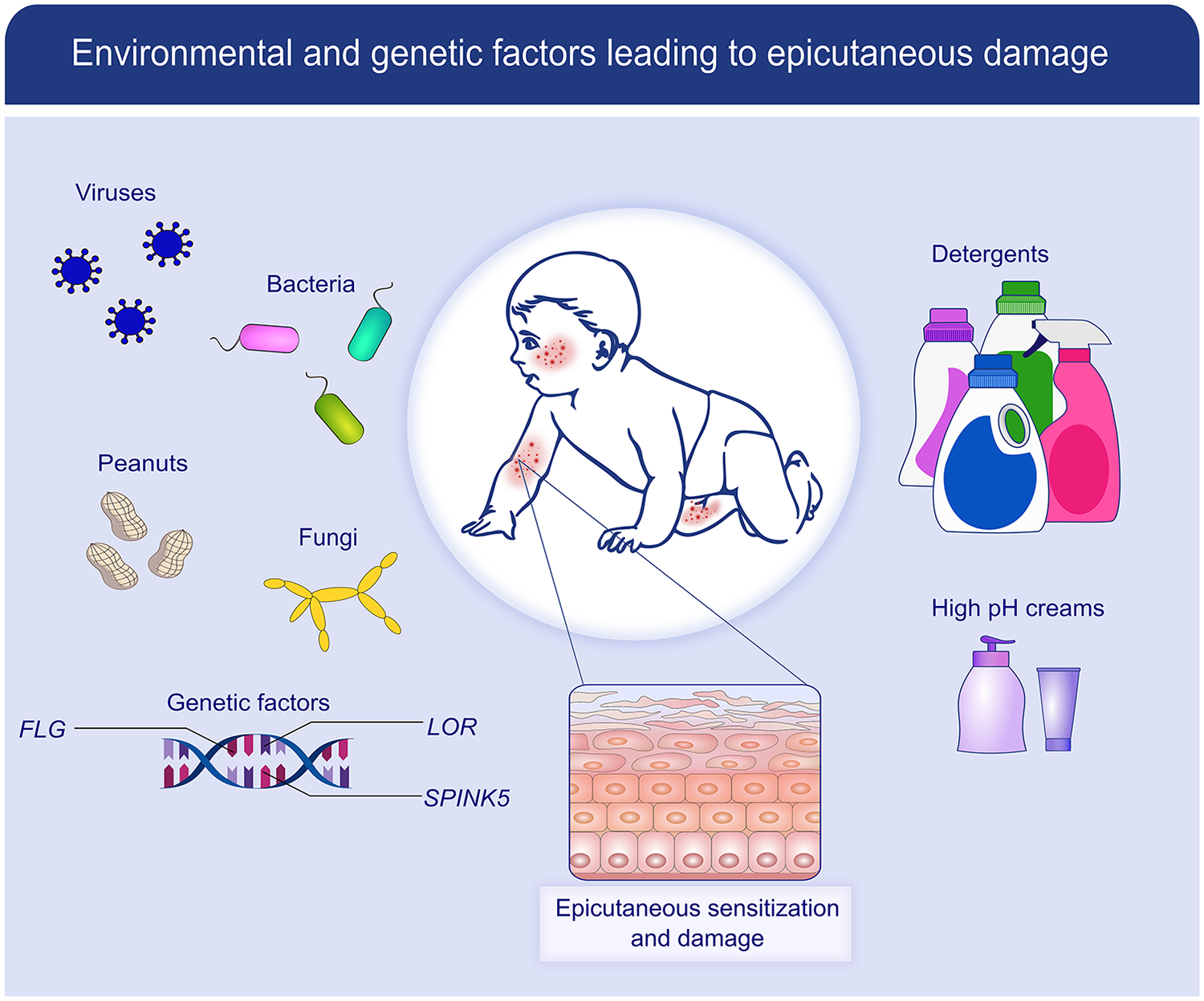
Factors leading to skin barrier dysfunction: The skin is constantly exposed to environmental factors, both natural (eg, bacteria, viruses, fungi, food and aero allergens) and man-made (e.g., detergents, high pH creams and lotions). In those genetically predisposed to allergic disease (e.g., filaggrin, SPINK5, and loricrin mutations), these factors lead to skin barrier dysfunction, epicutaneous damage, and allergic sensitization.
