Figure 9. Genetic background alters the sensitivity of heterozygous ND23 mutants to mortality from isoflurane and hyperoxia.
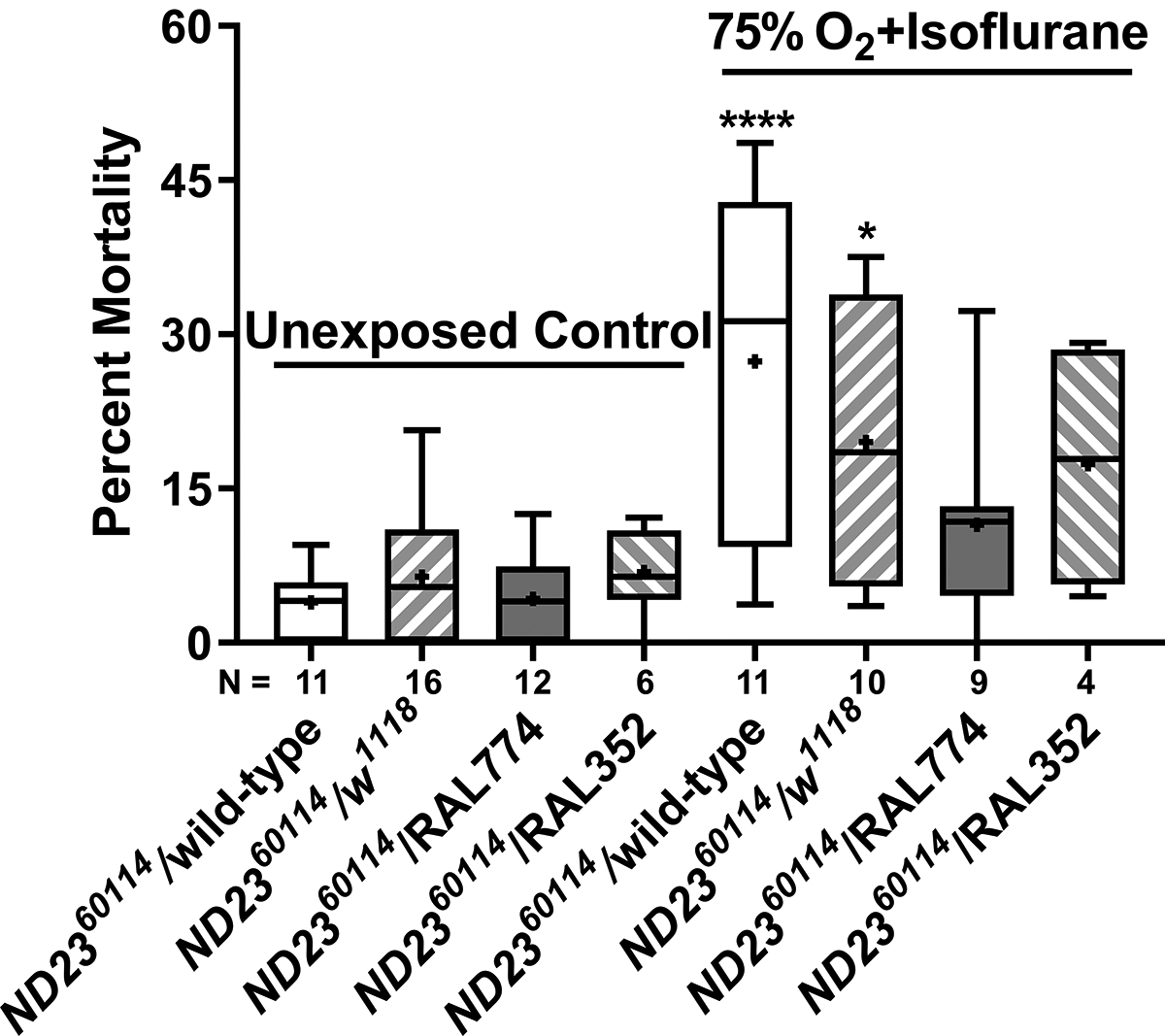
30–39-day-old females of the indicated genotypes were not exposed (Unexposed Control) or exposed to 2% isoflurane and 75% O2 for 2 h (75% O2 + isoflurane) and the percent mortality was determined at 24 h. Percent mortality in exposed flies increased for ND2360114/wild-type (P<0.0001) and ND2360114/w1118 (P=0.021) flies but not for ND2360114/RAL 774 (P=0.667) and ND2360114/RAL352 (P=0.671) flies. There was a significant effect of drug/genotype interaction (P=0.0435, two-way ANOVA). Males were not examined because not enough survived for biological replicates. Significance was determined using a two-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post-hoc test for multiple comparisons. *, P<0.05; ****, P<0.0001.
