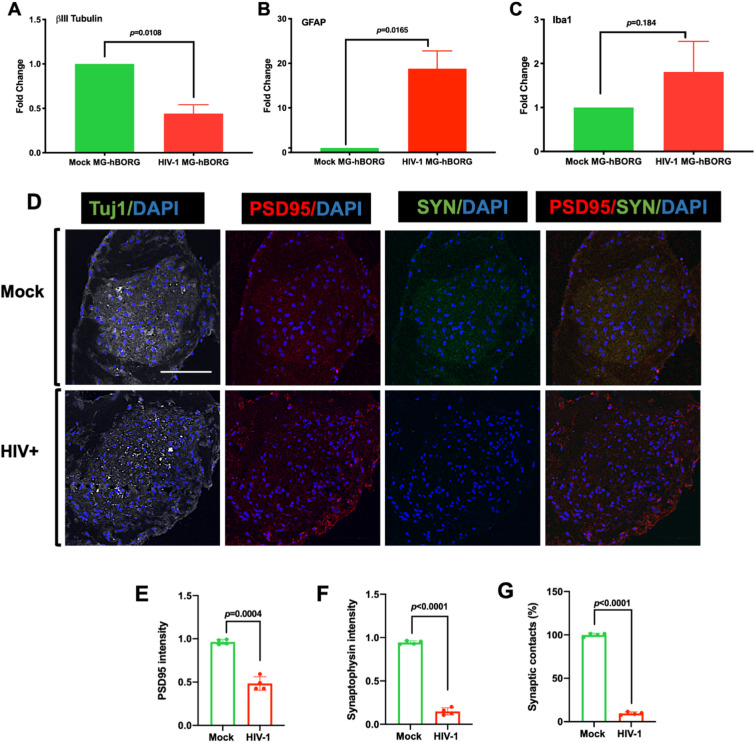
Figure 7.
HIV-1 infection of MG-hBORGs causes reactive astrocytosis, decreased synaptic density, and neurodegeneration. Expression levels of βIII-Tubulin (A), GFAP (B) and Iba1 (C) in HIV-infected and mock-infected MG-BORGs were assessed on day 15. Fold change in HIV-infected MG-hBORGs was calculated using mock-infected MG-hBORGs as 1 (N = 3). (D) Immunostaining of sections of MG-hBORGs for Tuj1(gray), PSD-95 (red) and SYN (green) were used to stain synapses (PSD95/SYN merged) in viable neurons in mock and HIV-infected organoids. Mean intensities PSD-95 (E) and SYN (F) were normalized to Tuj1 (maximum intensity). (G) The percentage of synaptic contacts (PSD-95/SYN co-localization intensity) in HIV-infected MG-hBORGs was calculated using the intensity of synaptic contacts in mock-infected MG-hBORGs as 100% (N = 4). Statistical significance was calculated using unpaired Student’s t test.