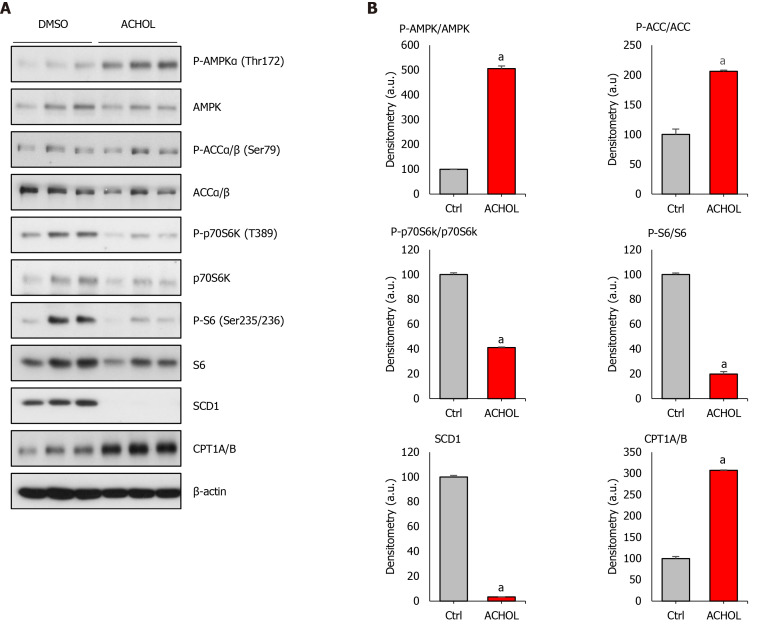
Figure 2.
Arachidyl amido cholanoic acid differentially regulates AMPK and mTORC1 in cultured hepatocytes. Mouse primary hepatocytes were isolated and allowed to attach for 3 h, after which culture medium was replaced by serum-free MEM with DMSO (vehicle) or Arachidyl amido cholanoic acid (Aramchol) (20 µM), and the cells were cultured for an additional 48 h. A: Effect of Aramchol treatment on SCD1, CPT1A/B, AMPK, P-AMPKα (Thr172), ACCα/β, P-ACCα/β (Ser79), p70S6K, P-p70S6K (T389), S6, and P-S6 (Ser235/236) protein levels in cultured mouse hepatocytes by Western blot analysis. β-actin was used as a loading control; B: Densitometric analysis of the Western blot protein levels. Effect of Aramchol treatment on the ratios of phosphorylated/total protein levels of AMPK, ACC and p70S6K is shown. In the case of SCD1 and CPT1A/B, the protein level is normalized against β-actin (loading control). Results are expressed as fold of total specific protein levels. At least triplicates were used per experimental condition. Data is shown as the mean ± SEM. aP < 0.05.