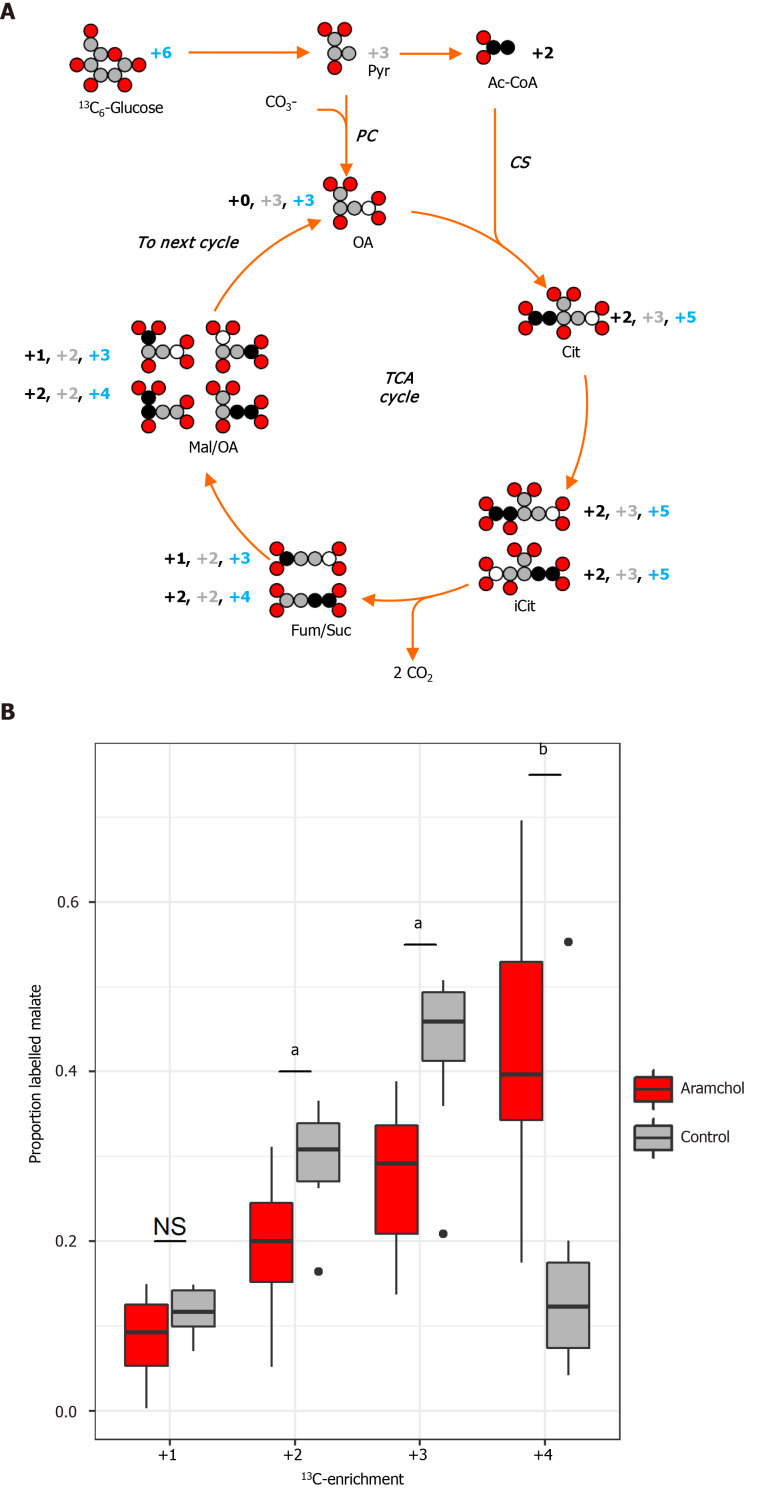
Figure 4.
Arachidyl amido cholanoic acid regulates tricarboxylic acid cycle activity. Glucose flux in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle was investigated in order to determine glucose utilization in the liver after arachidyl amido cholanoic acid (Aramchol) treatment (20 µmol/L). Murine hepatocytes were cultured with vehicle or Aramchol (20 µmol/L) for 48 h, after which uniformly labeled 13C6-glucose was added. A: Diagram of the label dispersion of fully 13C-labeled glucose for the initial cycle of the TCA cycle. Carbon atoms are either white, grey-shaded, or black depending on the origin of labelled and non-labelled carbons. Grey-shaded carbons originate directly from pyruvate (Pyr). Pyr is converted in oxaloacetate by pyruvate carboxylase after introduction of a carboxyl group coming from a carboxylate ion. Black coloured carbons originate from acetyl-CoA and are introduced via citrate synthase. White carbons are not labeled. The mass increases of the TCA cycle metabolites due to the incorporation of 13C are indicated and follow the same colour coding. The numbers indicated in blue are the total mass increase due to incorporation of labels via both pathways. Note that the formation of isocitrate (iCit) from citrate causes the formation of two distinct isotopomers because the hydroxyl group can shift equally likely to both sides. The formation of malate (Mal) from fumarate again doubles the amount of isotopomers for the same reason. In subsequent cycles, the isotopomer patterns take forms that are more complex. The transformation from iCit to succinate causes the loss of two carbon dioxide molecules; B: The 13C-label dispersion in the TCA cycle was determined by measuring the ratios of the different isotopomers of Mal at steady-state by mass spectrometry. After Aramchol treatment, an upregulation of the +4 labeled Mal species was found compared to control. aP < 0.002; bP < 0.0002 Aramchol treated vs control. TCA: Tricarboxylic acid; Pyr: Pyruvate; OA: Oxaloacetate; PC: Pyruvate carboxylase; CO3-: Carboxylate ion; Ac-CoA: Acetyl-CoA; CS: Citrate synthase; Cit: Citrate; iCit: Isocitrate; Mal: Malate; Fum: Fumarate; Suc: Succinate; CO2: Carbon dioxide.