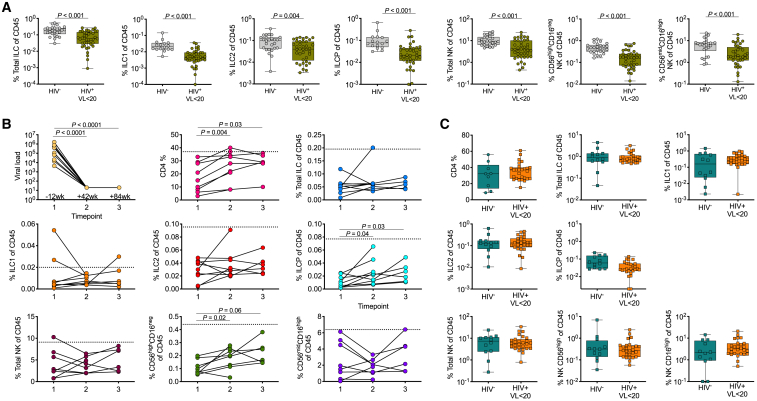
Figure 3.
Sustained Depletion of All Peripheral ILC and NK Subsets in Virally Suppressed Children in the Absence of Treatment Initiation at Birth
(A) Cross-sectional comparisons of all blood helper ILC and NK subsets in pediatric HIV-uninfected and virally suppressed (VL <20 HIV RNA copies/ml plasma) pediatric subjects treated for a median of 88 weeks (IQR 40–218) with median CD4% of 37 (IQR 26–35) and 30 (IQR 19–36), respectively.
(B) Longitudinal sampling of pediatric subjects (n = 9) before treatment initiation and at two time points after treatment intervention: time point 1 = 12 weeks before starting ART, time point 2 = 42 weeks after treatment, and time point 3 = 84 weeks after treatment when patients have fully suppressed plasma viral loads and reconstituted CD4 percentages (see also Figure S1). The dotted lines represent normal levels of HIV-negative pediatric subjects.
(C) Blood CD4, helper ILC, and NK subset percentages in HIV-uninfected infants aged 2–5 years (infant HIV−; n = 12; petrol) and HIV+ and viral-suppressed (VL <20 HIV RNA copies/ml plasma) infants aged 0.2–3 years (infant HIV+; n = 27; orange).
p values by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test.