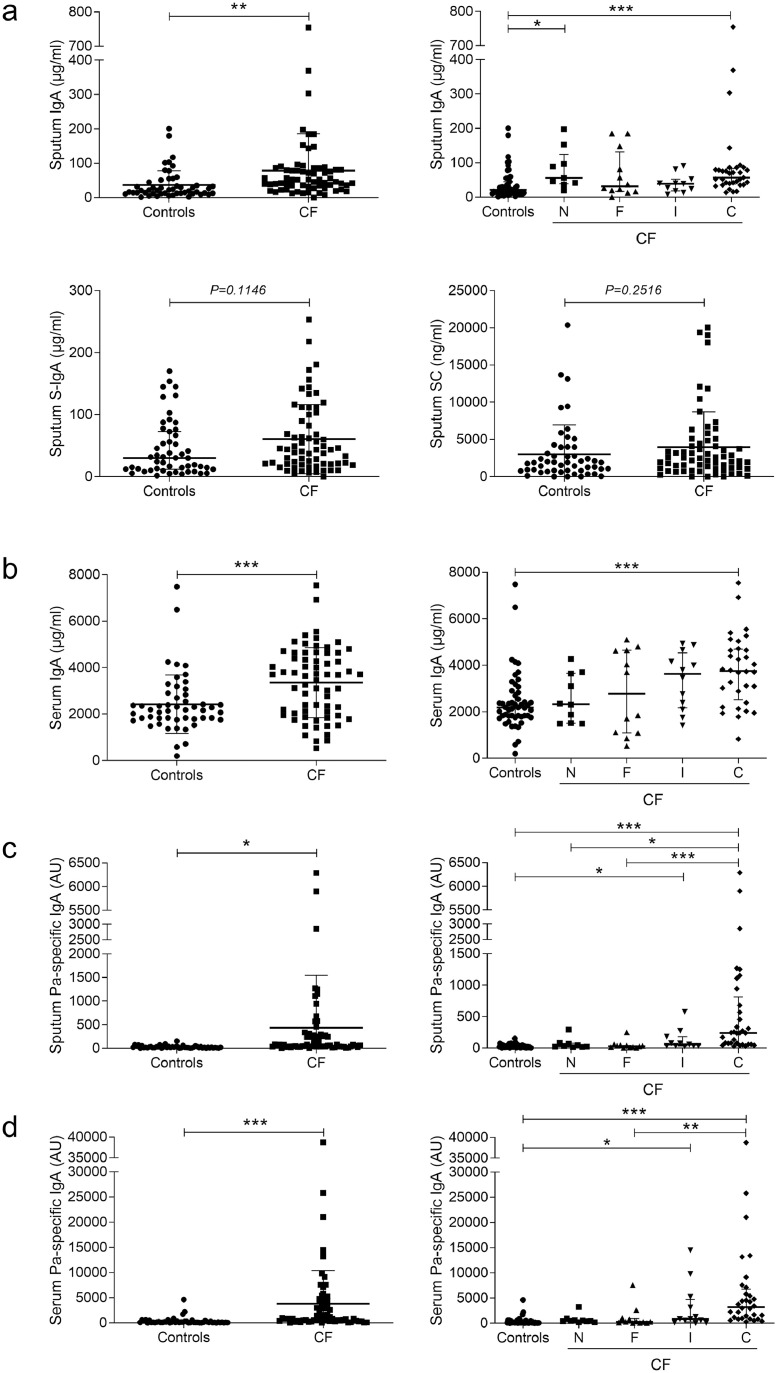
Fig. 3.
IgA and Pa-specific IgA concentrations are increased in sputum and serum from patients with CF. (a) IgA concentration in sputum from 51 controls and 65 patients with CF (**p = 0.0092, unpaired Student's t-test), distributed following Leeds criteria (***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's test); S-IgA concentration in sputum from 51 controls and 65 patients with CF (p = 0.1146, unpaired Student's t-test); SC concentration in sputum from 51 controls and 65 patients with CF (p = 0.2516, unpaired Student's t-test). (b) IgA concentration in serum from 51 controls and 66 patients with CF (***p = 0.0006, unpaired Student's t-test), distributed following Leeds criteria (***p < 0.001, Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's test). (c) Pa-specific IgA concentration in sputum from 51 controls and 65 patients with CF (*p = 0.0107, unpaired Student's t-test), distributed following Leeds criteria (***p < 0.001, *p < 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's test). (d) Pa-specific IgA concentration in serum from 51 controls and 66 patients with CF (***p = 0.0003, unpaired Student's t-test), distributed following Leeds criteria (***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's test). Bars indicate mean and standard deviation or median and interquartile ranges (Leeds distribution). IgA, immunoglobulin A; Pa, Pseudomonas aeruginosa; CF, cystic fibrosis; S-IgA, secretory immunoglobulin A; SC, secretory component; C, chronically infected by Pa; I, intermittently infected by Pa; F, free of Pa infection; N, never infected with Pa.