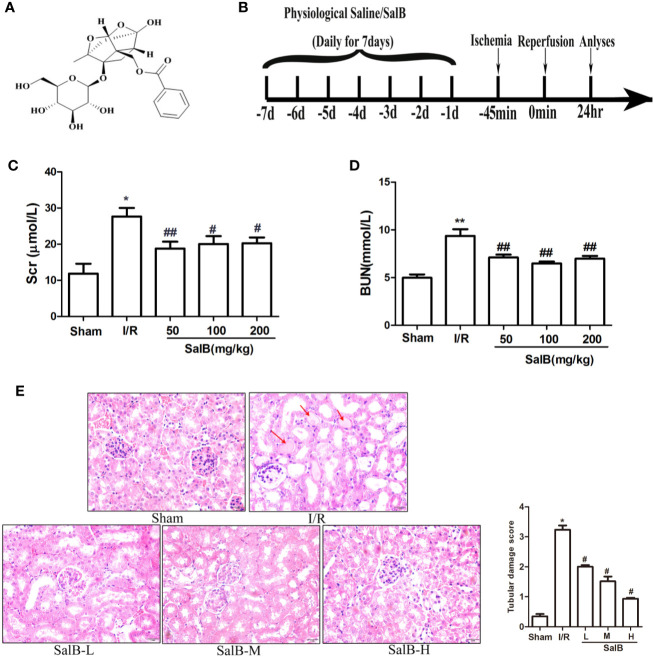
Figure 1.
SalB treatment ameliorates renal function and renal tubule pathological injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion (I/R). (A) The chemical structure of Salvianolic acid B (SalB). (B) Experimental design. (C, D) Serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels. The data show means ± SEM (n = 6).*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. sham group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. I/R group. (E) Kidney tissue sections were subjected to histological examination by hematoxylin and eosin staining (H&E) to evaluate renal tubule injury; protein casts are shown with the red arrow. Tubular damage was scored in a double-blind manner method based on the percentage of injury included tubular dilation and intertubular hemorrhage: 0, no damage; 1, < 25%; 2, 25 ~ 50%; 3, 50 ~ 75%; 4, > 75%) Magnification: 400×.