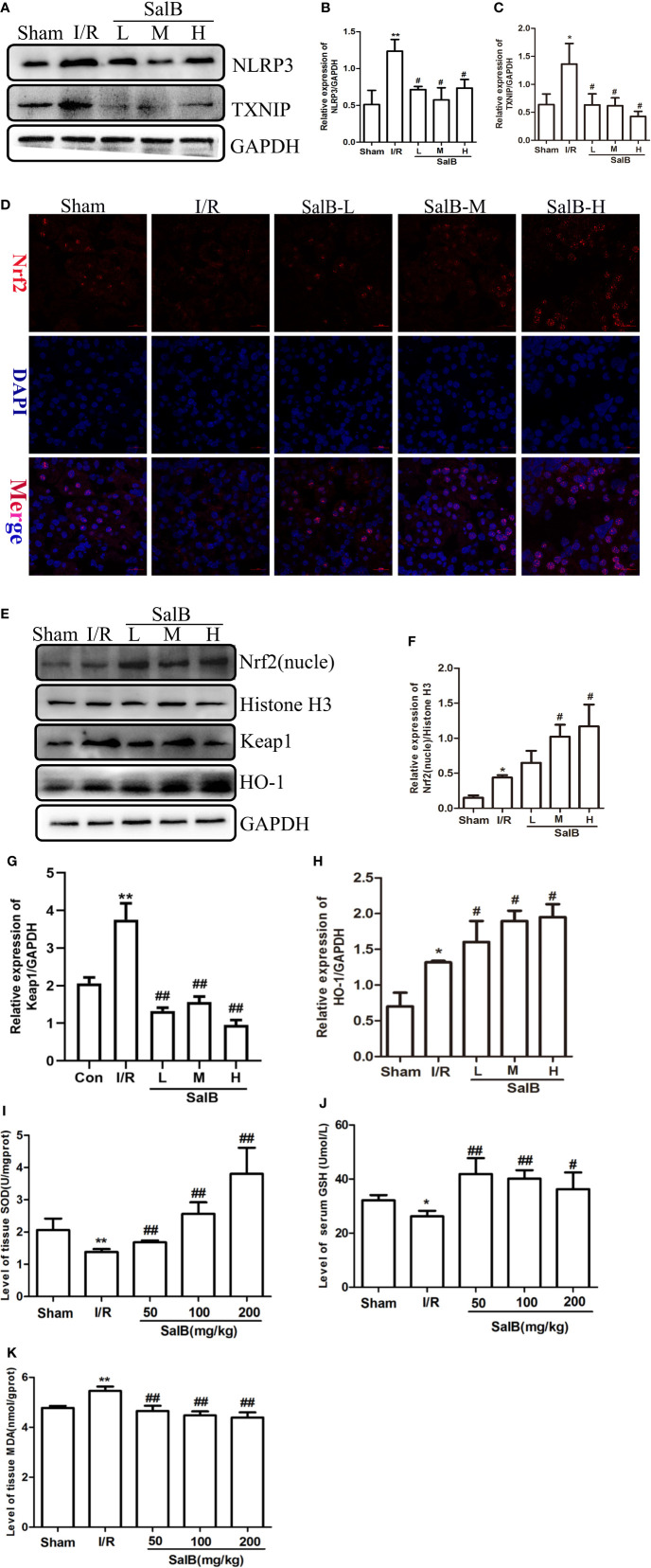
Figure 4.
Salvianolic acid B (SalB) promotes Nrf2 nuclear activation and inhibits NLR family pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3)/thioredoxin-interacting protein-thioredoxin1 (TXNIP) expression in ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) mice. (A–C) The expression of NLRP3 and TXNIP. (D) Immunofluorescence images (magnification ×200) showing the nuclear expression and localization of Nrf2 in the Sham, I/R, SalB-L, SalB-M, SalB-H groups. Blue: nuclear staining (DAPI); red: Nrf2; staining. Scale bar: 20 μm. (E) Representative western blots and (F–H) quantification of relative protein expression for nuclear Nrf2, keap1 and HO-1. (I–K) Superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione (GSH), and malondialdehyde (MDA) detected by a microplate reader. Data are represented as images or expressed as the mean ± SEM of each group from three separate experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. sham group; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 vs. I/R group.