Figure 2.
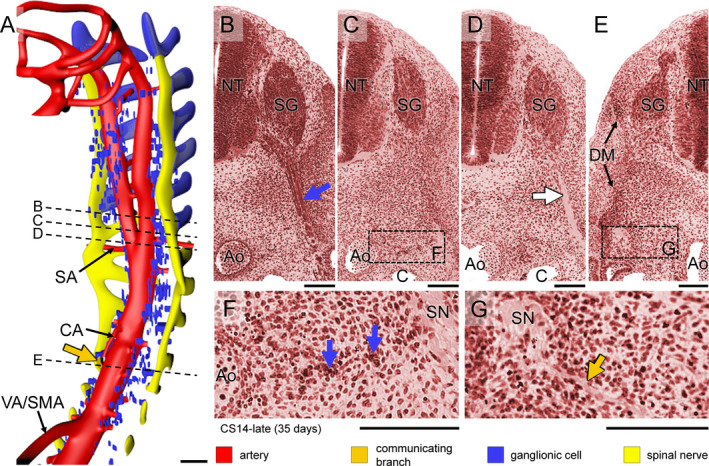
Formation of sympathetic trunks and communicating branches in a CS14‐late embryo (~35 days). Panel (a) shows the distribution of ganglionic cells with the ventral roots of spinal nerves and dorsal aorta from C1 to T5 (see also Figure S3B). Panels (b–e) show transverse sections from cranial to caudal as indicated by dotted lines in panel (a). Panels (f and g) show magnified views of the rectangles in panels (c and e), respectively. In this embryo, Schwann cell precursors cells migrate along the ventral roots of spinal nerves as intensely staining strands in the cervical region (blue cover on spinal roots in panel (a) and blue arrow in panel (b)), but not further caudally (pale nerve strand; white arrow in panel (d)). Ganglionic cells (blue arrows) are also present between the dorsal aorta (Ao) and spinal nerves (SN) in this area (panel f). Furthermore, nerve fibres extend medially following the route of ganglionic cells as communicating branches in the upper thoracic region (dark‐yellow arrow in panels [a,g]). Bars (a) = 200 µm; (b–g) = 100 µm [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
