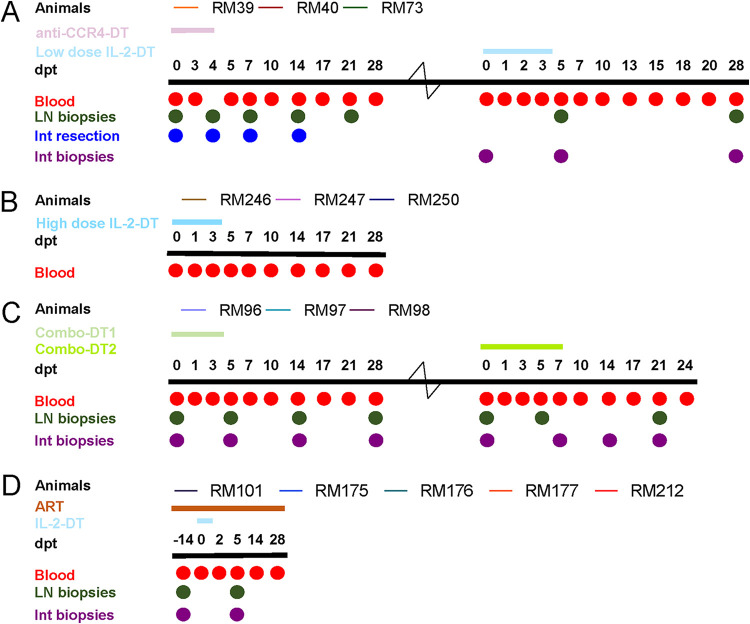
FIG 1.
Experimental design of the study. Fourteen rhesus macaques (RMs) were infected i.v. with 300 TCID50 SIVsab92018, and they were allowed to robustly control virus replication. Then, after >1 year of viral control, three RMs received anti-CCR4-diphtheria toxin (DT) and low-dose IL-2-DT (A), three RMs received a high-dose IL-2-DT (B), and three RMs received combinations of anti-CCR4-DT and IL-2-DT in a ratio of 1.62:1 by weight (Combo-DT1) and in a ratio of 1:1.62 (Combo-DT2) (C). Finally, five RM controllers received 14 days of antiretroviral therapy (ART), followed by the administration of the low-dose IL-2-DT on ART (D). After each treatment, the animals were monitored for an average of 28 days posttreatment (dpt). Treg-depleting immunotoxin administrations are illustrated as color-coded lines over each study group. Blood, lymph node (LN), and duodenal biopsy specimens were collected at numerous experimental points, as indicated by the circles.