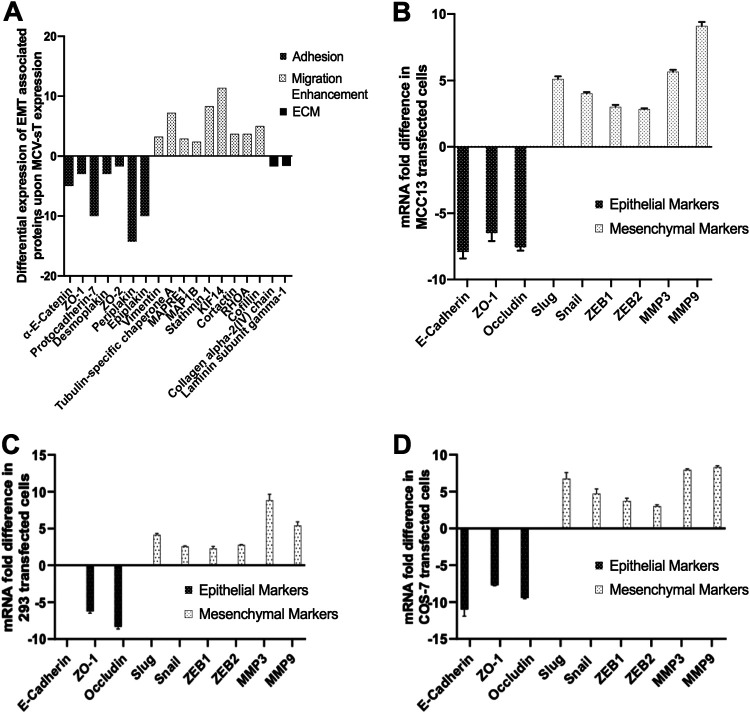
FIG 1.
MCV sT leads to differential expression of proteins associated with epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT). (A) Quantitative proteomics analysis illustrating differential expression of EMT-associated proteins upon MCV sT expression. The i293-sT cells were grown in DMEM with unlabeled arginine and lysine amino acids (R0K0) and induced (IN) for 24 h or grown in DMEM with labeled amino acids (R6K4) and remained uninduced (UN) (25). Proteins associated with cell adhesion and structural integrity of the extracellular matrix were downregulated upon MCV sT expression, while expression of proteins involved in cell migration by reorganization of the actin network and microtubule destabilization were upregulated. (B) MCV sT regulates EMT-associated gene expression. MCC13 cells were transfected with control or MCV sT plasmids. While epithelial markers were downregulated, mesenchymal markers were significantly upregulated upon MCV sT expression. Cellular RNA was extracted using a TRIzol reagent, and transcript levels were analyzed by RT-qPCR using the comparative ΔΔCT method (n = 3). HEK293 (C) and COS-7 (D) cells were transfected with control or MCV sT plasmids. While epithelial markers were downregulated, mesenchymal markers were significantly upregulated upon MCV sT expression. E-cadherin expression levels were not assessed in HEK293 cells due to low expression. Cellular RNA was extracted using a TRIzol reagent, and transcript levels were analyzed by RT-qPCR using the comparative ΔΔCT method (n = 3).