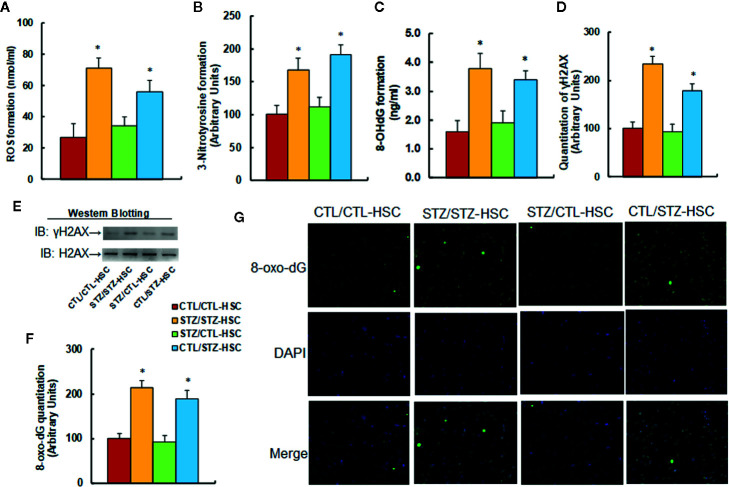
Figure 3.
Transplantation of bone marrow HSC reverses maternal diabetes-induced oxidative stress in PBMC in autistic offspring. The 6-week-old male offspring from either the control (CTL) or maternal diabetes (STZ) groups received transplantation of bone marrow HSC from either the control (CTL-HSC) or maternal diabetes (STZ-HSC) group, and the mice were used for further biomedical analysis 5 weeks after transplantation. (A) ROS formation in PBMC, n = 5. (B) Quantitation of 3-nitrotyrosine formation, n = 5. (C) 8-OHdG formation, n = 5. (D) Quantitation of γH2AX formation. (E) Representative γH2AX western blotting band for (D), n = 5. (F) Quantitation of 8-oxo-dG formation, n = 5. (G) Representative pictures of 8-oxo-dG staining for oxidative stress (green) and DAPI staining for nuclei (blue) in PBMC, n = 4. *P < 0.05, vs. CTL/CTL-HSC group. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM.