Fig. 10.
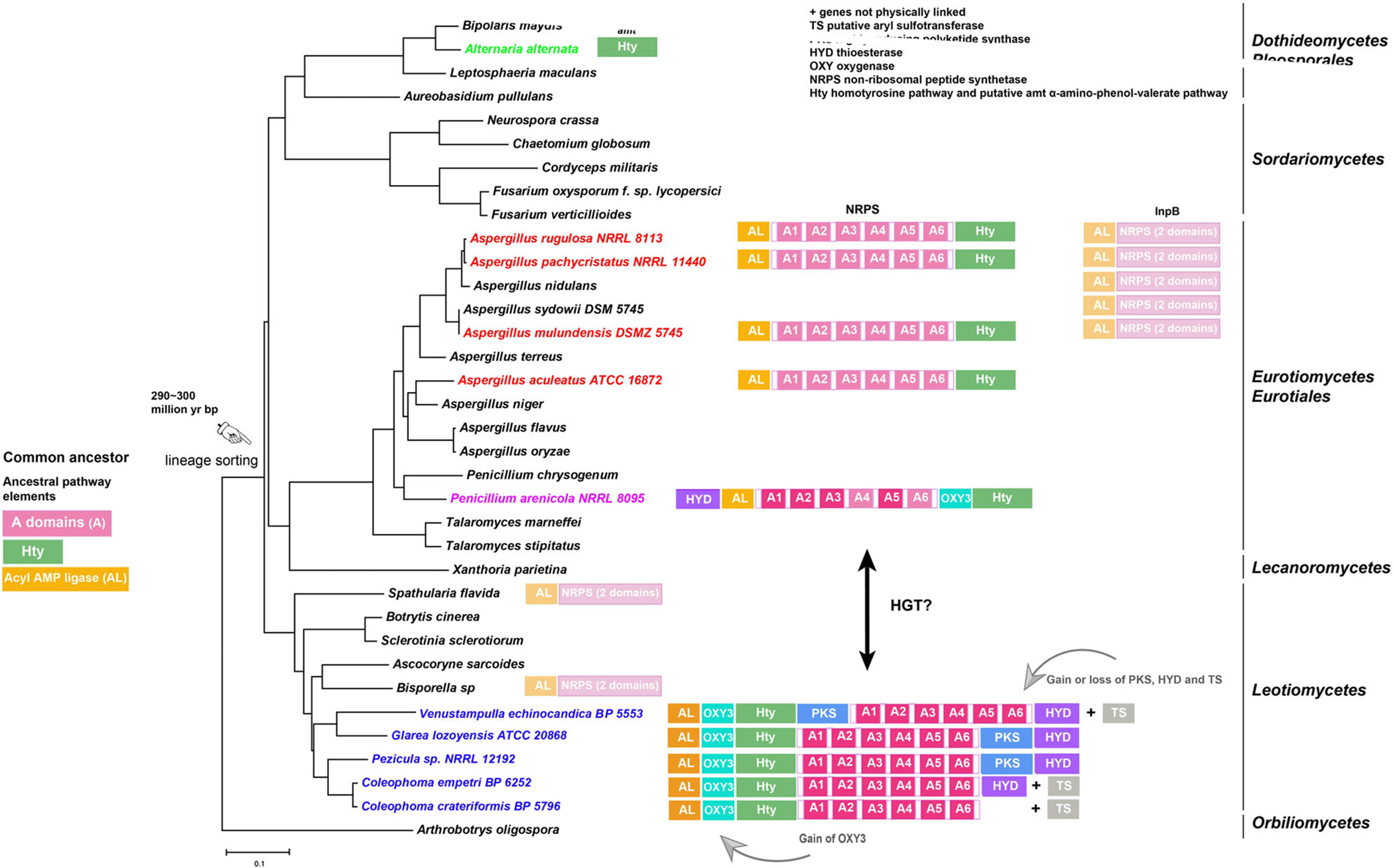
Evolutionary hypothesis for the family of echinocandin and fellutamide biosynthetic gene clusters. Possible ancestral elements observed in the Aspergillaceae include adenylation domains on the NRPSs, an acyl-CoA ligase of the fellutamide and echinocandin pathways and their orthologues, and the Hty pathway. The origin of the Hty pathway is unknown, and it is illustrated separately from the core NRPS of the echinocandins. In the Leotiomycete lineage, a mutation in A domain 5 leads to incorporation of glutamine in position 5, and an oxygenase for glutamine hydroxylation (OXY3) and a thioesterase (HYD) were recruited. A highly reducing PKS and a presumed aryl sulfotransferase (TS) were recruited in some species of the Leotiomycetes. An arrow indicates the possible origin of the acrophiarin gene cluster in Penicillium arenicola by horizontal transfer (HGT) from Leotiomycetes. The date of the estimated divergence of Leotiomycete–Eurotiomycete lineages is from Lutzoni and colleagues (2018).
