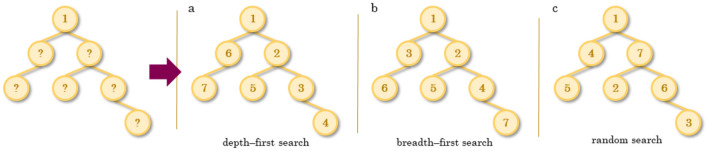
Fig. 2.
Graph traversal algorithms. Three widespread graph traversal algorithms are illustrated above for an example branched graph. The numbers correspond to the order in which the nodes are explored, starting at node 1. a A depth-first search first explores each “branch” of a graph to the fullest extent, then goes back and explores branches at the last branched node, until all branches have been explored. b A breadth-first search first explores all nearest neighbours of a node, and then the nearest neighbours of the nearest neighbours, and so on, until the whole graph has been explored. c A random search explores nodes in the graph in an arbitrary order, regardless of how they are connected