Figure 6.
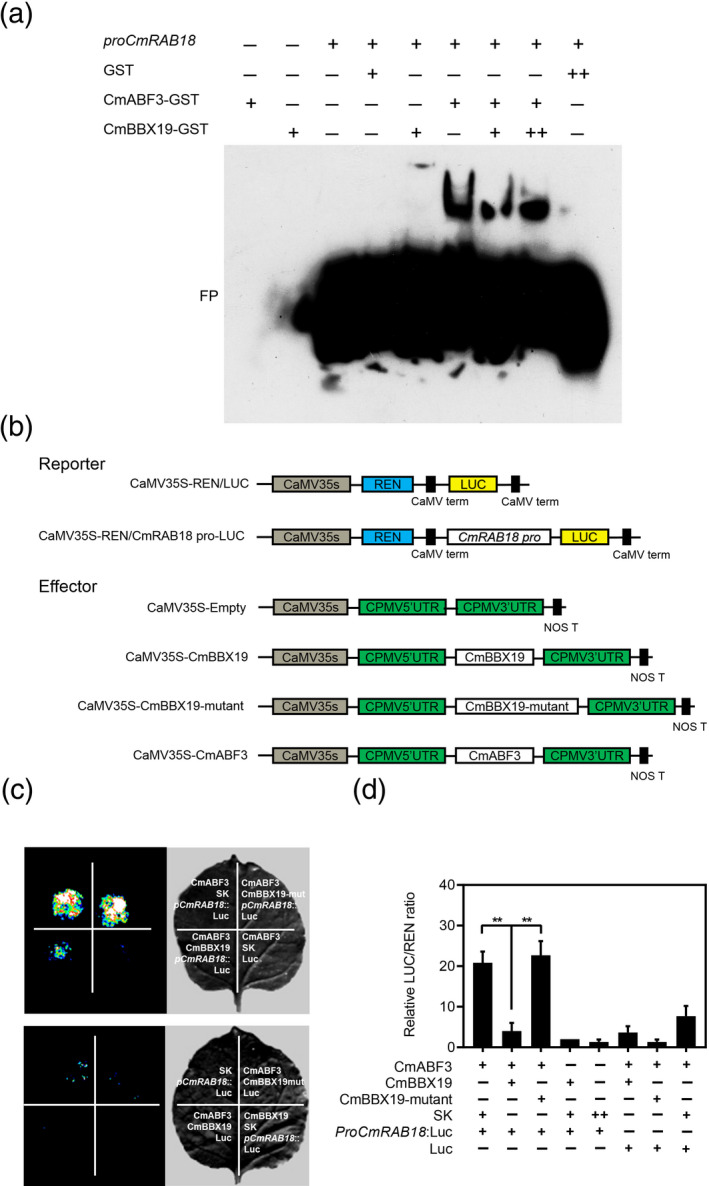
CmBBX19 interacts with CmABF3 to repress transcription of CmRAB18.
(a) Analysis of CmABF3 and CmBBX19 binding to the CmRAB18 promoter, based on an electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Purified protein (3 μg) was incubated with 50 nm biotin‐labeled probe. For the competition test, purified CmBBX19 protein, at 1‐ or 10‐fold concentrations, was added to the experiment described above. FP, free probe.
(b) Schematic representation of the double‐reporter and effector plasmids used in the dual‐luciferase reporter assay.
(c‐d) The interaction of CmABF3 or CmBBX19 with the CmRAB18 promoter as shown by a dual luciferase (LUC) reporter system. A 445 bp CmRAB18 promoter fragment was used. Constructs used in the assay are shown above. LUC vectors containing the renilla luciferase (REN) gene under the control of the 35S promoter were used as a positive control. Samples were infiltrated into Nicotiana benthamiana leaves, and LUC and REN activities were assayed 3 days after infiltration. Representative photographs are shown of firefly luciferase fluorescence signals (c) and relative LUC/REN ratio are shown of normalizing LUC activity to that of REN (d) when the corresponding effectors and reporters were introduced into N. benthamiana leaves. Three independent experiments were performed and error bars indicate standard deviations. Asterisks indicate significant differences as determined by Tukey’s honestly significant difference method (**P < 0.01).
