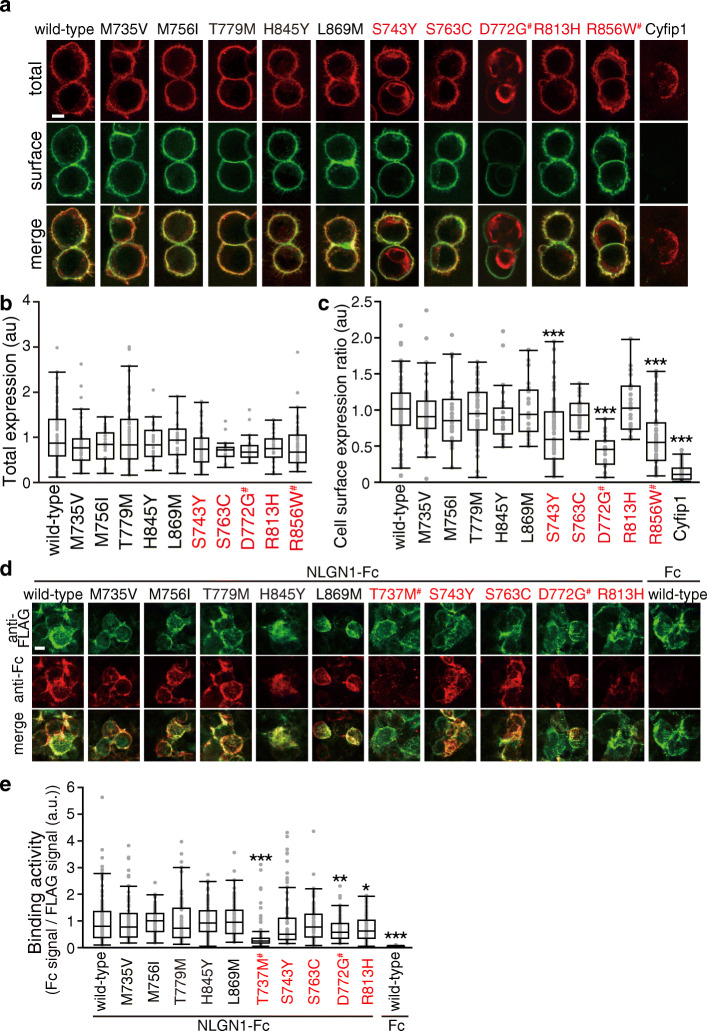
Fig. 4.
Characterization of NRXN1α variants in LNS4 domain on cell surface expression and NLGN1 interaction. a Representative images of HEK293T cells expressing wild-type and disease-associated and non-associated NRXN1α-LNS4 variants tagged with FLAG epitope. Cell surface and total NRXN1α are shown in green and red, respectively. FLAG-tagged cyfip1, a cytoplasmic protein, serves as a negative control. b and c Total expression levels (b) and ratios of cell surface and total expression levels (c) of wild-type and LNS4 variants of NRXN1α in a (n = 24–87 HEK293T cells). d Binding of the extracellular domain of NLGN1 fused to Fc to HEK293T cells transfected with FLAG-tagged NRXN1α LNS4 variants (green). Cell surface-bound Fc fusion proteins were visualized using anti-Fc antibody (red). e Ratios of staining signals for NLGN1-Fc and FLAG-tagged NRXN1α variants in d (n = 66–170 HEK293T cells). Scale bars, 10 μm in a and d. All data are presented as box plots. Horizontal line in each box shows median, box shows the interquartile range (IQR), and the whiskers are 1.5× IQR. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001, Tukey’s test compared with wild-type NRXN1α-expressing cells in c and compared with wild-type NRXN1α-expressing cells incubated with NLGN1-Fc in e. Disease-associated and non-associated variants are colored in red and black, respectively in b, c, and e. #, variants identified in this study