Figure 3.
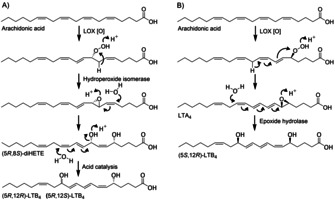
A) Proposed pathway for the formation of LTB4 isomers in algae. Arachidonic acid is oxygenated by an 8R‐LOX to yield a hydroperoxy‐fatty acid. This intermediate is then cyclized to the epoxide by a hydroperoxide isomerase followed by stereoselective enzymatic addition of water giving rise to (5R,8S)‐diHETE. Under acidic conditions, this precursor rearranges to (5R,12R/S)‐LTB4 (ee=95 %). B) Mammalian biosynthesis of (5S,12R)‐LTB4. Arachidonic acid is initially oxygenated by a 5S‐LOX forming 5‐HPETE that is subsequently dehydrated resulting in the precursor epoxide LTA4. This is then enzymatically hydrolyzed to LTB4.38, 39
