FIGURE 2.
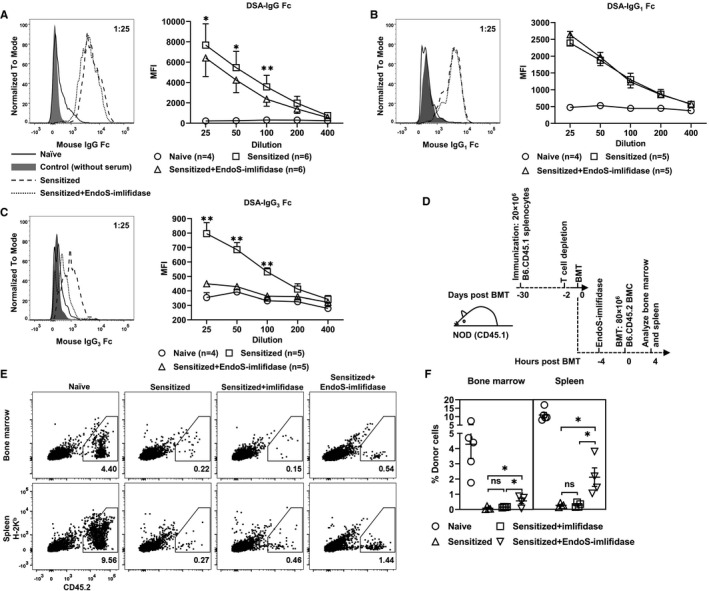
Endoglycosidase of Streptococcus pyogenes (EndoS)‐imlifidase reduces donor‐specific antibodies (DSA)‐mediated killing of donor bone marrow cells (BMC) in sensitized recipients. A‐C, Naive NOD mice were immunized with FVB splenocytes 4 weeks prior to the administration of EndoS‐imlifidase. Sera were harvested prior to immunization, prior to and 4 h after enzyme treatment. Representative histograms on the left are for DSA‐IgG Fc (panel A), DSA‐IgG1 Fc (panel B), DSA‐IgG3 Fc (panel C), and DSA‐IgG3 heavy chain (panel D) with sera at a 1:25 dilution. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of DSA in the titrated sera is shown on the right. Mean ± SEM are shown. Ratio paired t test was used to compare MFI of DSA before and after enzyme treatment at each serum dilution with *P < .05, **P < .01. D, Schematic of the experiment shown in E,F. Naive NOD mice were immunized with B6.CD45.1 splenocytes 4 weeks prior to injection of T cell–depleting mAbs. EndoS‐imlifidase was administrated 2 d post‐T cell depletion. Four hours after enzyme treatment, NOD mice were injected with 80 million B6.CD45.2 BMC intravenously. Splenocytes and BMC were analyzed for the expression of MHC‐I H‐2Kb and CD45.2. E,F, Shown are representative dot plots of the four different treatment groups (on the left) and the percentage of donor cells (on the right, mean ± SEM). One‐way analysis of variance with Holm‐Sidak's multiple comparisons were used to compare values between the three sensitized groups with *P < .05
