Fig. 2.
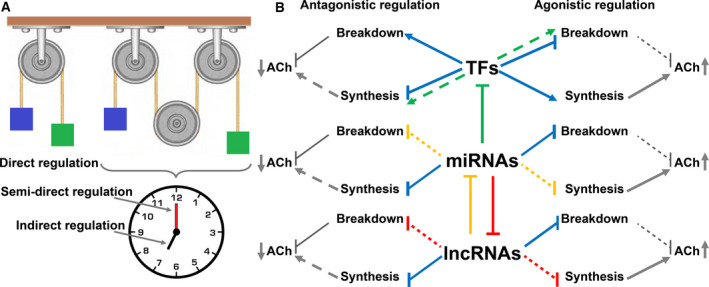
Types and forms of ncRNA regulation over the cholinergic tone. (A) Immediate regulation of cholinergic transcripts by ncRNA (one wheel) is referred to as ‘direct’, unlike the effect of lncRNAs over ACh signaling, which is mediated via other ncRNAs or TFs (three wheels). This may occur rapidly (the clock’s minutes hand), in which case it is referred to as ‘semidirect regulation’, or slowly (hours hand), to be defined ‘indirect regulation’. (B) TFs, miRNAs, and lncRNAs can each cause either agonistic (right hand side) or antagonistic (left hand side) regulation. Triangle arrows (→) indicate induction, and straight‐line arrows (Ⱶ) indicate suppression. Blue lines indicate innate features of the TF\miRNA\lncRNA, whereas the red, green, and yellow lines indicate complex systems in which a full line leads to the effect shown by the scattered lines. For example, when miRNAs repress enhancing TFs (green full line), they cease to induce genes involved in ACh breakdown (e.g., AChE, green scattered line to the right). This weakens the effect on ACh breakdown (leading to elevated ACh levels) [26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31]. Note that each of the ncRNA types may affect the impact of the other types.
